Feedthrough
Feedthrough[edit]
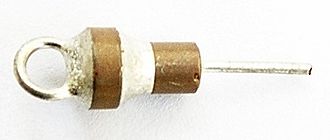
A feedthrough is a device used to pass electrical signals or power through an enclosure or barrier, such as a wall or bulkhead, while maintaining the integrity of the barrier. Feedthroughs are essential components in various applications, including vacuum chambers, pressure vessels, and electronic enclosures, where they allow for the transmission of electrical signals or power without compromising the environmental conditions inside the enclosure.
Types of Feedthroughs[edit]
Feedthroughs can be classified based on their application, construction, and the type of signals they carry. Common types include:
Electrical Feedthroughs[edit]
Electrical feedthroughs are designed to carry electrical signals or power. They are often used in vacuum technology and high-voltage applications. These feedthroughs must be carefully designed to prevent electrical arcing and to maintain insulation integrity.
Optical Feedthroughs[edit]
Optical feedthroughs are used to transmit optical signals through a barrier. They are commonly used in fiber optic systems and require precise alignment to ensure signal integrity.
Fluid Feedthroughs[edit]
Fluid feedthroughs allow for the passage of liquids or gases through a barrier. They are used in chemical processing and biotechnology applications where maintaining a controlled environment is crucial.
Construction and Materials[edit]
Feedthroughs are constructed using materials that match the requirements of their specific application. Common materials include:
- Metals: Such as stainless steel and copper, which provide strength and conductivity.
- Ceramics: Used for their insulating properties and ability to withstand high temperatures.
- Polymers: Such as PTFE and PEEK, which offer chemical resistance and flexibility.
The choice of material depends on factors such as the operating environment, the type of signals being transmitted, and the mechanical stresses involved.
Applications[edit]
Feedthroughs are used in a wide range of applications, including:
- Vacuum Systems: To maintain a vacuum while allowing electrical connections to be made to devices inside the chamber.
- High-Pressure Environments: Such as submarines and aerospace applications, where maintaining pressure integrity is critical.
- Medical Devices: Where feedthroughs are used to connect sensors and actuators inside the body to external monitoring equipment.
Design Considerations[edit]
When designing a feedthrough, several factors must be considered:
- Seal Integrity: Ensuring that the feedthrough maintains the barrier's integrity against leaks.
- Electrical Performance: Minimizing signal loss and crosstalk for electrical feedthroughs.
- Thermal Management: Managing heat dissipation, especially in high-power applications.
Related Pages[edit]
Ad. Transform your life with W8MD's Budget GLP-1 injections from $75


W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Weight loss injections in NYC (generic and brand names):
- Zepbound / Mounjaro, Wegovy / Ozempic, Saxenda
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $75 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointmentsNYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian