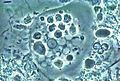
Entamoeba gingivalis
Entamoeba gingivalis is a species of amoebae that is primarily found in the human mouth, residing in the gingival pockets near the base of the teeth. It is notable for being the first amoeba in humans to be described, with its discovery dating back to 1849 by Gros. Unlike its relative Entamoeba histolytica, which can cause the disease amoebiasis, E. gingivalis is not known to be a pathogenic amoeba, meaning it does not typically cause disease in humans.
Characteristics[edit]
Entamoeba gingivalis is a non-flagellated, non-cyst-forming amoeba, which differentiates it from other species of Entamoeba. It measures approximately 10 to 35 micrometers in diameter and exhibits a granular endoplasm. The amoeba feeds on bacteria and other debris found within the oral cavity, particularly in the gingival pockets surrounding the teeth. Its presence is often associated with poor oral hygiene and periodontal disease, although it does not directly cause these conditions.
Life Cycle[edit]
The life cycle of Entamoeba gingivalis is relatively simple compared to other protozoans, as it does not form cysts and exists solely in the trophozoite form. Transmission occurs through direct contact, often via saliva or dental procedures. Due to its habitat being restricted to the oral cavity, it does not undergo the complex life cycle stages seen in other Entamoeba species, which involve cyst formation and fecal-oral transmission.
Clinical Significance[edit]
While Entamoeba gingivalis is not considered pathogenic, its presence is often indicative of poor oral health. It has been found in higher concentrations in individuals with gum disease, such as gingivitis and periodontitis, suggesting a correlation between E. gingivalis colonization and oral health conditions. However, it is not clear whether the amoeba contributes to the progression of these diseases or simply thrives in the altered environment caused by them.
Diagnosis and Treatment[edit]
Diagnosis of Entamoeba gingivalis infection is typically made through microscopic examination of dental plaque or gingival pocket material. Special stains may be used to differentiate E. gingivalis from other oral amoebae and bacteria. Treatment is not usually necessary for E. gingivalis itself, but maintaining good oral hygiene and treating any underlying periodontal disease is important for overall oral health.
Prevention[edit]
Preventive measures against Entamoeba gingivalis colonization include regular dental check-ups, proper oral hygiene practices such as brushing and flossing, and avoiding the sharing of utensils or other items that may come into contact with saliva. These measures can also help prevent a range of other oral health issues.
See Also[edit]
-
Entamoeba gingivalis microscopy
-
Entamoeba gingivalis
-
Entamoeba gingivalis phagocytosis
Ad. Transform your life with W8MD's Budget GLP-1 injections from $49.99


W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Weight loss injections in NYC (generic and brand names):
- Zepbound / Mounjaro, Wegovy / Ozempic, Saxenda
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $49.99 for the starting dose of Semaglutide and $65.00 for Tirzepatide.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointmentsNYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian