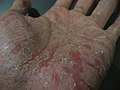
Dyshidrosis

Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD's medical weight loss NYC, sleep center NYC
Philadelphia medical weight loss and Philadelphia sleep clinics
| Dyshidrosis | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Synonyms | Pompholyx, dyshidrotic eczema, vesicular eczema |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | Dermatology |
| Symptoms | Itchy blisters on palms, soles, and fingers |
| Complications | N/A |
| Onset | Young adulthood |
| Duration | Weeks to months |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Unknown, possibly allergies, stress, or sweating |
| Risks | Atopic dermatitis, hay fever, asthma |
| Diagnosis | Clinical examination |
| Differential diagnosis | Contact dermatitis, scabies, psoriasis |
| Prevention | N/A |
| Treatment | Moisturizers, steroid creams, phototherapy |
| Medication | N/A |
| Prognosis | N/A |
| Frequency | ~5-20 per 10,000 people per year |
| Deaths | N/A |
Dyshidrosis, also known as dyshidrotic eczema or pompholyx, is a type of dermatitis characterized by the appearance of small, itchy blisters on the palms of the hands and soles of the feet.<ref>
Berger, TG.
Dyshidrotic Eczema(link).
NCBI Bookshelf.
</ref> These blisters, generally one to two millimeters in size, heal over the course of three weeks, but may frequently recur. Although redness is not typically present, repeated bouts can result in skin thickening and fissures.
Symptoms and Diagnosis[edit]
The primary symptom of dyshidrosis is the formation of blisters filled with fluid, accompanied by intense itching, which may become painful if left untreated. Over time, these blisters may become larger, merge together, and eventually dry out, leading to cracked and peeling skin. Skin thickening, or hyperkeratosis, may occur as a result of chronic, repeated episodes.<ref>Wollina, U,
Pompholyx: a review of clinical features, differential diagnosis, and management, Am J Clin Dermatol, 2010, DOI: 10.2165/11533270-000000000-00000, PMID: 20874631,</ref>
Diagnosis is generally made based on the appearance of the skin and reported symptoms. There are no specific lab tests to confirm dyshidrosis, but physicians may perform patch testing or skin biopsies if necessary to rule out other possible conditions, such as fungal infections or psoriasis.
Causes and Triggers[edit]
The exact cause of dyshidrosis is unknown, but it is thought to be related to allergic reactions and the body's immune response. Certain factors can trigger or worsen the condition, including:
- Stress
- Exposure to certain metals, such as nickel and cobalt
- Fungal infections
- Skin exposure to water or moist environments<ref>Guillet, MH,
A 3-year causative study of pompholyx in 120 patients, Arch Dermatol, 2007, DOI: 10.1001/archderm.143.12.1504, PMID: 17576941,</ref>
Treatment[edit]
The primary goal of treatment for dyshidrosis is to alleviate itching and prevent new blisters from forming. Treatment options include:
- Topical steroids to reduce inflammation
- Antihistamines to relieve itching
- Immunosuppressant drugs, such as cyclosporine or methotrexate, for severe cases
- Ultraviolet light therapy (phototherapy)
- Emollients or moisturizers to help keep skin hydrated<ref>Veien, NK,
The clinical course of pompholyx: a follow-up study, Arch Dermatol, 2001, DOI: 10.1001/archderm.137.3.280, PMID: 11255424,</ref>
- Lifestyle modifications, such as avoiding known triggers and keeping the skin clean and dry, can also help manage symptoms and reduce the frequency of flare-ups.
Gallery[edit]
-
Dyshidrotic dermatitis on hands, late stage
-
Dyshidrosis
-
Palmar dyshidrosis, peeling stage
-
Dyshidrosis, late stage
-
Rim of scale on plantar surface of thumb
Ad. Transform your life with W8MD's Budget GLP-1 injections from $49.99


W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Weight loss injections in NYC (generic and brand names):
- Zepbound / Mounjaro, Wegovy / Ozempic, Saxenda
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $49.99 for the starting dose of Semaglutide and $65.00 for Tirzepatide.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointmentsNYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian