Craniofacial surgery
Craniofacial surgery is a specialized branch of plastic surgery that deals with the correction of congenital and acquired deformities of the skull, face, and jaw. This field encompasses a wide range of procedures aimed at restoring or improving the function and appearance of the head and face region. Craniofacial surgery is often multidisciplinary, involving collaboration with neurosurgeons, otolaryngologists, dentists, and other specialists to address complex anatomical and functional issues.
History[edit]
The origins of craniofacial surgery can be traced back to the early 20th century, with significant advancements occurring in the mid-1900s. Pioneers like Paul Tessier, who is often referred to as the father of craniofacial surgery, expanded the boundaries of the field by developing techniques to safely operate on the bones of the face and skull. These innovations laid the groundwork for the modern practices used today.
Indications[edit]
Craniofacial surgery is indicated for a variety of conditions, including, but not limited to:
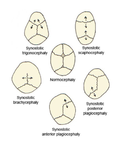
- Craniosynostosis, the premature fusion of one or more cranial sutures, leading to abnormal head shape and potentially affecting brain development.
- Cleft lip and palate, congenital deformities affecting the upper lip and the roof of the mouth.
- Craniofacial tumors, both benign and malignant growths within the craniofacial region.
- Traumatic injuries, such as fractures of the facial bones or skull.
- Syndromic craniosynostosis, such as Apert, Crouzon, and Pfeiffer syndromes, which involve multiple cranial sutures and are often associated with other physical and developmental issues.
Procedures[edit]
Craniofacial surgery encompasses a variety of surgical techniques, including:
- Cranial vault remodeling, a procedure to reshape the skull and allow for normal brain growth in patients with craniosynostosis.
- Distraction osteogenesis, a method to gradually lengthen bones, often used in the jaw or midface to correct congenital or acquired deformities.
- Le Fort osteotomies, surgical procedures to correct midface anomalies or deformities.
- Orbital surgery, which addresses abnormalities of the eye sockets and surrounding structures.
- Rhinoplasty, surgery to correct and reconstruct the nose, which may be performed for aesthetic or functional reasons.
Risks and Complications[edit]
As with any surgical procedure, craniofacial surgery carries risks. These may include infection, bleeding, nerve damage, and the need for additional surgeries. The complexity of craniofacial procedures and the critical structures involved necessitate a highly skilled surgical team to minimize risks and manage complications.
Recovery and Rehabilitation[edit]
Recovery from craniofacial surgery varies depending on the specific procedure and the individual patient. It often involves hospitalization, pain management, and a period of rest at home. Rehabilitation may include physical therapy, speech therapy, and other supportive measures to enhance functional outcomes.
Future Directions[edit]
Advancements in technology, such as 3D printing and virtual surgical planning, are revolutionizing craniofacial surgery. These tools allow for more precise planning and execution of surgical procedures, potentially reducing operative time and improving outcomes.
Craniofacial_surgery[edit]
-
Sutures from top view
-
Single suture synostosis
-
Incision locations for advancement
-
Bone segments removed in fronto-supraorbital advancement
Ad. Transform your life with W8MD's Budget GLP-1 injections from $49.99


W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Weight loss injections in NYC (generic and brand names):
- Zepbound / Mounjaro, Wegovy / Ozempic, Saxenda
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $49.99 for the starting dose of Semaglutide and $65.00 for Tirzepatide.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointmentsNYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian