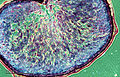
Caryopsis
Caryopsis is a type of fruit commonly referred to as a grain. It is characteristic of the Poaceae family, which includes well-known cereal crops such as wheat, rice, corn, barley, and oats. A caryopsis is distinguished by its simple, dry nature, and unlike many other fruits, it does not split open at maturity. The key feature of a caryopsis is the fusion of the seed coat with the fruit wall, or pericarp, making the seed and fruit indistinguishable.
Characteristics[edit]
The caryopsis is small and hard, adapted for various dispersal mechanisms, including wind and animal ingestion. The outer layer, or pericarp, is fused to the seed coat, a unique characteristic among fruits. This fusion aids in protecting the inner embryo and endosperm, which are crucial for the germination and growth of a new plant. The endosperm within the caryopsis is a significant source of starch, making these grains a vital food source for humans and animals.
Ecological and Economic Importance[edit]
Caryopses are of immense ecological and economic importance. They serve as a primary food source for a significant portion of the world's population. Crops like wheat and rice are staple foods in many cultures, providing essential nutrients and calories. Additionally, these grains are used in various industries, including food production, alcohol brewing, and biofuel manufacturing.
Cultivation[edit]
The cultivation of caryopsis-bearing plants has a long history, with evidence of farming dating back thousands of years. Modern agriculture has developed sophisticated methods for growing, harvesting, and processing these grains, allowing for efficient production to meet global demand. However, challenges such as pests, diseases, and climate change pose ongoing threats to crop yields and food security.
Research and Breeding[edit]
Significant research efforts are dedicated to understanding the genetics and biology of caryopsis-producing plants. These studies aim to improve yield, disease resistance, and nutritional content through traditional breeding and genetic modification. Advances in biotechnology have led to the development of crop varieties that can withstand adverse environmental conditions, such as drought and salinity, which are increasingly important in the face of climate change.
Conclusion[edit]
The caryopsis is a vital component of the human diet and the global economy, with a profound impact on agriculture and food systems worldwide. Ongoing research and development efforts are crucial to ensuring the sustainability and security of these essential food sources.
-
Assorted grains
-
Spiklet
-
Caryopsis cross-section
Ad. Transform your life with W8MD's Budget GLP-1 injections from $75


W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Weight loss injections in NYC (generic and brand names):
- Zepbound / Mounjaro, Wegovy / Ozempic, Saxenda
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $75 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointmentsNYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian