Carbon-dioxide laser
A type of gas laser using carbon dioxide as the lasing medium
Carbon Dioxide Laser[edit]
The carbon dioxide laser (CO2 laser) is a type of gas laser that uses a mixture of carbon dioxide, nitrogen, and helium as its lasing medium. It is one of the earliest gas lasers to be developed and remains one of the most useful. The CO2 laser is known for its high efficiency and high power output, making it a popular choice in industrial, medical, and military applications.

Principle of Operation[edit]
The CO2 laser operates by exciting carbon dioxide molecules to a higher energy state. This is achieved by passing an electric current through the gas mixture, which typically consists of carbon dioxide, nitrogen, and helium. The nitrogen molecules are excited by the electric discharge and transfer energy to the carbon dioxide molecules, which then emit infrared light at a wavelength of 10.6 micrometers when they return to their ground state.
The laser action occurs when the emitted photons stimulate other excited CO2 molecules to emit more photons of the same wavelength, resulting in a coherent beam of light. The laser cavity, which consists of mirrors at each end, amplifies this light through multiple reflections, producing a powerful laser beam.
Applications[edit]
CO2 lasers are widely used in various fields due to their ability to cut, weld, and engrave materials with precision. In the industrial sector, they are commonly used for cutting and welding metals, plastics, and other materials. The high power output and efficiency of CO2 lasers make them ideal for these applications.
In the medical field, CO2 lasers are used in surgery for cutting and vaporizing soft tissues. They are particularly useful in dermatology for skin resurfacing and in otolaryngology for procedures involving the throat and vocal cords.
In the military, CO2 lasers are used in range-finding and target designation systems due to their ability to produce a focused beam over long distances.
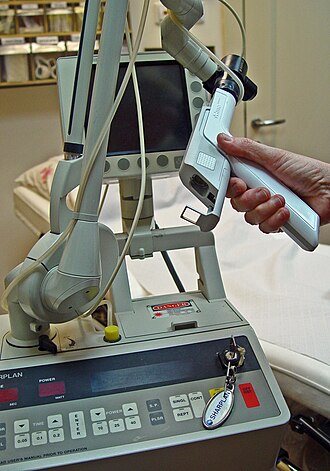
Advantages and Disadvantages[edit]
The CO2 laser is highly efficient, with efficiencies of up to 20%. It can produce continuous wave (CW) or pulsed laser beams, making it versatile for different applications. The long wavelength of the CO2 laser allows it to be absorbed by many materials, making it effective for cutting and engraving.
However, the CO2 laser also has some disadvantages. The equipment can be bulky and requires careful handling due to the high voltages involved. Additionally, the infrared wavelength is not visible to the human eye, necessitating the use of special safety equipment to prevent accidental exposure.
Related Pages[edit]
Ad. Transform your life with W8MD's Budget GLP-1 injections from $75


W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Weight loss injections in NYC (generic and brand names):
- Zepbound / Mounjaro, Wegovy / Ozempic, Saxenda
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $75 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointmentsNYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian