Canine space
Canine Space[edit]
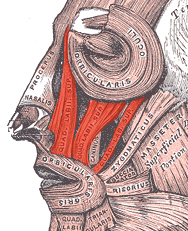
The canine space is an anatomical area located in the face, specifically in the region of the upper jaw. It is a potential space that can become clinically significant in cases of infection or trauma. Understanding the boundaries, contents, and clinical implications of the canine space is important for medical professionals, particularly those in the fields of dentistry, maxillofacial surgery, and otolaryngology.
Anatomy[edit]
The canine space is situated superior to the canine fossa, which is a depression in the maxilla above the canine tooth. It is bordered by several important anatomical structures:
- Superiorly: The space is bounded by the infraorbital margin and the levator labii superioris muscle.
- Inferiorly: It is limited by the oral cavity and the buccinator muscle.
- Medially: The boundary is formed by the nasal cavity and the nasalis muscle.
- Laterally: The space is bordered by the zygomaticus major muscle and the zygomatic bone.

Contents[edit]
The canine space contains:
- The infraorbital nerve, which is a branch of the maxillary nerve (CN V2).
- The infraorbital artery and vein, which supply blood to the region.
- Fatty tissue that provides cushioning and support to the surrounding structures.
Clinical Significance[edit]
The canine space can become involved in various pathological conditions, most notably infections. An infection in this space can arise from:
- Dental infections: Particularly those involving the maxillary canine tooth, which can spread to the canine space.
- Trauma: Injury to the face can lead to hematoma or abscess formation in the canine space.
Infections in the canine space can present with swelling of the upper lip and cheek, pain, and sometimes fever. If left untreated, the infection can spread to adjacent spaces, leading to more serious complications such as orbital cellulitis or cavernous sinus thrombosis.
Diagnosis and Treatment[edit]
Diagnosis of canine space infections typically involves clinical examination and imaging studies such as CT scan or MRI to assess the extent of the infection. Treatment may include:
- Antibiotics: To treat the underlying infection.
- Surgical drainage: In cases where an abscess has formed, surgical intervention may be necessary to drain the pus.
Related Pages[edit]
Ad. Transform your life with W8MD's Budget GLP-1 injections from $75


W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Weight loss injections in NYC (generic and brand names):
- Zepbound / Mounjaro, Wegovy / Ozempic, Saxenda
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $75 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointmentsNYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian