Bioremediation of radioactive waste
Bioremediation of Radioactive Waste is a process that uses biological organisms, primarily microbes, to transform or neutralize radioactive waste. This process is a subset of bioremediation, a broader field that uses biological organisms to clean up various types of environmental pollutants.
Overview[edit]
Radioactive waste is a byproduct of various industrial processes such as nuclear power generation, nuclear medicine, and nuclear weapons production. It poses significant environmental and health risks due to its long-lasting radioactivity. Traditional methods of managing radioactive waste include containment, isolation, and long-term storage. However, these methods are often costly, technically challenging, and pose their own environmental risks.
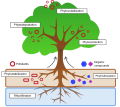
Bioremediation of radioactive waste offers a potential alternative to these traditional methods. It involves the use of organisms, primarily microbes, that can interact with radioactive materials in ways that render them less harmful. These interactions can include processes such as biosorption, bioaccumulation, and biotransformation.
Mechanisms[edit]
The mechanisms of bioremediation of radioactive waste involve complex biochemical processes. Some microbes can absorb radioactive materials onto their cell surfaces, a process known as biosorption. Others can accumulate radioactive materials within their cells, a process known as bioaccumulation. Still others can transform radioactive materials into less harmful forms, a process known as biotransformation.
Applications[edit]
Bioremediation of radioactive waste has been applied in various settings, including contaminated soil and water. It has also been explored for use in the cleanup of nuclear accidents, such as the Chernobyl disaster and the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear disaster.
Challenges and Future Directions[edit]
Despite its potential, bioremediation of radioactive waste faces several challenges. These include the need for a better understanding of the underlying microbial processes, the development of effective delivery systems for the microbes, and the management of potential risks associated with the use of genetically modified organisms. Future research in this field is likely to focus on addressing these challenges and exploring new applications for this promising technology.

This article is a environment-related stub. You can help WikiMD by expanding it!
Bioremediation of radioactive waste[edit]
-
Three plants irradiated with a fourth as the control
-
Enzymatic reduction of radionuclides
-
Biosorption, biomineralization and bioaccumulation of radionuclides
-
Chernikovite
-
Evolution of the Old Rifle Processing Site
-
Deinococcus radiodurans
-
Phytoremediation Process
-
Reedbeds
Ad. Transform your life with W8MD's Budget GLP-1 injections from $49.99


W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Weight loss injections in NYC (generic and brand names):
- Zepbound / Mounjaro, Wegovy / Ozempic, Saxenda
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $49.99 for the starting dose of Semaglutide and $65.00 for Tirzepatide.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointmentsNYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian