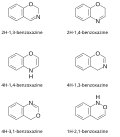
Benzoxazine
Benzoxazine is a heterocyclic compound consisting of a benzene ring fused to an oxazine ring. This chemical structure forms the backbone of various synthetic polymers and small molecules used in a wide range of applications, from advanced materials engineering to pharmaceuticals. The unique properties of benzoxazine-based polymers, such as their thermal stability, mechanical strength, and chemical resistance, make them suitable for high-performance applications in aerospace, automotive, and electronics industries.
Chemistry[edit]
Benzoxazine is characterized by its chemical formula, which typically involves a benzene ring (C6H6) fused with an oxazine ring, a six-membered ring containing one oxygen and one nitrogen atom. The general formula for benzoxazine compounds can be represented as C8H7NO, although variations exist depending on the substitution pattern on the rings. The synthesis of benzoxazine monomers involves the reaction of phenols, formaldehyde, and primary amines. This reaction proceeds via a Mannich reaction mechanism, leading to the formation of the benzoxazine ring through an intramolecular cyclization process.
Properties and Applications[edit]
Benzoxazine resins are known for their outstanding thermal properties, including high glass transition temperatures and thermal stability. These materials exhibit low shrinkage upon polymerization, which is a critical factor in maintaining dimensional stability in composite materials. Additionally, benzoxazine-based polymers are inherently flame retardant, making them ideal for applications requiring high fire resistance.
In the field of pharmaceuticals, certain benzoxazine derivatives have been explored for their biological activities, including antimicrobial, antifungal, and anticancer properties. The ability to modify the benzoxazine core structure allows for the design of molecules with specific biological activities, making them potential candidates for drug development.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability[edit]
Recent research has focused on the development of bio-based benzoxazine monomers, derived from renewable resources such as lignin, cardanol, and vanillin. These bio-based polymers aim to reduce the environmental impact associated with the production and disposal of synthetic polymers. The use of natural phenolic compounds in the synthesis of benzoxazine resins represents a sustainable approach to polymer science, contributing to the advancement of green chemistry and materials science.
Conclusion[edit]
Benzoxazine and its derivatives represent a versatile class of compounds with significant potential in various high-performance applications. The ongoing research and development in the synthesis, characterization, and application of benzoxazine-based materials are expected to lead to innovative solutions in materials science, engineering, and pharmaceuticals, addressing some of the critical challenges in these fields.
-
Benzoxazine examples
Ad. Transform your life with W8MD's Budget GLP-1 injections from $75


W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Weight loss injections in NYC (generic and brand names):
- Zepbound / Mounjaro, Wegovy / Ozempic, Saxenda
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $75 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointmentsNYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian