B vitamins
B vitamins are a class of water-soluble vitamins that play important roles in cell metabolism and synthesis of red blood cells. Though these vitamins share similar names (B1, B2, B3, etc.), they are chemically distinct compounds that often coexist in the same foods. In general, dietary supplements containing all eight are referred to as a vitamin B complex. Individual B vitamin supplements are referred to by the specific number or name of each vitamin, such as B1 for thiamine, B2 for riboflavin, and B3 for niacin, as examples. Some are more commonly recognized by name than by number: niacin, pantothenic acid, biotin and folate.
List of B vitamins[edit]
Each of the B vitamins has a unique role in the body and is essential for maintaining overall health:
- B1 (Thiamine): Thiamine helps convert nutrients into energy, supports healthy nerve function, and plays a role in the production of neurotransmitters.
- Sources: Whole grains, legumes, pork, and nuts.
- B2 (Riboflavin): Riboflavin is necessary for energy production, cellular function, and the metabolism of fats and drugs.
- Sources: Milk, cheese, eggs, leafy greens, and fortified cereals.
- B3 (Niacin): Niacin helps in energy production, DNA repair, and supports the health of the skin, nervous system, and digestive system.
- Sources: Meat, fish, poultry, whole grains, and fortified cereals.
- B5 (Pantothenic Acid): Pantothenic acid is crucial for the synthesis of fatty acids, cholesterol, and hormones, as well as energy production.
- Sources: Meat, poultry, fish, whole grains, legumes, and avocados.
- B6 (Pyridoxine): Pyridoxine is involved in amino acid metabolism, neurotransmitter synthesis, and the production of hemoglobin.
- Sources: Meat, fish, poultry, legumes, and bananas.
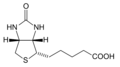
- B7 (Biotin): Biotin is essential for the metabolism of carbohydrates, fats, and proteins, as well as healthy hair, skin, and nails.
- Sources: Egg yolks, nuts, seeds, and salmon.
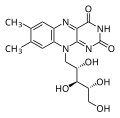
- B9 (Folate or Folic Acid): Folate is vital for DNA synthesis, cell division, and proper brain function. It is particularly important during pregnancy for the healthy development of the fetus.
- Sources: Leafy greens, legumes, fortified cereals, and citrus fruits.
- B12 (Cobalamin): Cobalamin is crucial for red blood cell formation, DNA synthesis, and the maintenance of nerve function.
- Sources: Animal products such as meat, fish, poultry, eggs, and dairy products. Fortified cereals and nutritional yeast are also sources for vegans and vegetarians.
A well-balanced diet typically provides sufficient amounts of B vitamins. However, some individuals, such as older adults, pregnant women, and those with certain medical conditions or on specific medications, may require supplements to meet their daily requirements.
|
|
|
| Vitamins (A11) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| Malnutrition | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
B vitamins[edit]
-
Thiamin
-
Riboflavin
-
Niacin
-
Pantothenic acid
-
Pyridoxal phosphate
-
Biotin
-
Folic acid
-
Cobalamin
Ad. Transform your life with W8MD's Budget GLP-1 injections from $49.99


W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Weight loss injections in NYC (generic and brand names):
- Zepbound / Mounjaro, Wegovy / Ozempic, Saxenda
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $49.99 for the starting dose of Semaglutide and $65.00 for Tirzepatide.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointmentsNYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian