Auditory brainstem response
The Auditory Brainstem Response (ABR) is a neurophysiological measure of the brain's electrical activity in response to sound. It is used primarily to assess hearing and neurological function. The ABR test is non-invasive and involves placing electrodes on the scalp to record the brain's activity in response to auditory stimuli, typically clicks or tone bursts.
Physiology[edit]
The ABR reflects the activity of the auditory nerve and the brainstem pathways. When a sound is heard, it travels through the outer ear, middle ear, and inner ear, where it is converted into electrical signals by the cochlea. These signals are then transmitted via the auditory nerve to the brainstem, where they are processed by various nuclei, including the cochlear nucleus, superior olivary complex, and inferior colliculus.
Clinical Applications[edit]
ABR testing is used in several clinical settings:
- Newborn Hearing Screening: ABR is commonly used to screen newborns for hearing loss. Early detection of hearing impairment is crucial for timely intervention and development of language skills.
- Diagnostic Hearing Testing: In individuals who cannot provide reliable behavioral responses, such as infants or those with developmental disabilities, ABR can objectively assess hearing thresholds.
- Neurological Assessment: ABR can help diagnose neurological disorders affecting the auditory pathways, such as acoustic neuroma or multiple sclerosis.
Procedure[edit]
During an ABR test, the patient typically lies down in a quiet room. Electrodes are placed on the scalp and earlobes or mastoid bones. Headphones or ear inserts deliver the auditory stimuli. The test usually takes 30 minutes to an hour, and the patient needs to remain still and relaxed.
Interpretation[edit]
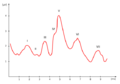
The ABR waveform consists of several peaks, labeled I through VII, which correspond to neural activity at different points along the auditory pathway. The latency and amplitude of these peaks are analyzed to assess auditory function. Delays or abnormalities in the waveform can indicate hearing loss or neurological issues.
Advantages and Limitations[edit]
ABR is advantageous because it is objective, non-invasive, and can be used in patients who are unable to cooperate with traditional hearing tests. However, it requires specialized equipment and trained personnel to administer and interpret the results.
Related Pages[edit]
-
Auditory brainstem response
Ad. Transform your life with W8MD's Budget GLP-1 injections from $75


W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Weight loss injections in NYC (generic and brand names):
- Zepbound / Mounjaro, Wegovy / Ozempic, Saxenda
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $75 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointmentsNYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian