Aspergillus tubingensis
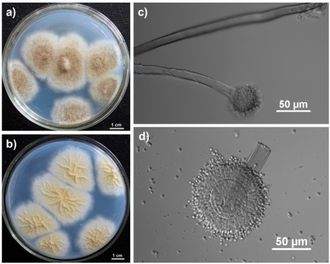
Aspergillus tubingensis is a species of fungus in the genus Aspergillus. It is a member of the Aspergillus niger group, which is known for its industrial and environmental significance. This species was first described in 1934 by Thom and Raper.
Description[edit]
Aspergillus tubingensis is a filamentous fungus that forms black colonies. It is morphologically similar to Aspergillus niger, but can be distinguished by its unique genetic and biochemical characteristics. The conidia of A. tubingensis are typically globose to subglobose and have a rough surface.
Habitat and Ecology[edit]
Aspergillus tubingensis is commonly found in soil and decaying organic matter. It has been isolated from various environments, including agricultural fields, compost, and indoor environments. This species is known for its ability to degrade a wide range of organic materials, making it an important organism in biodegradation and bioremediation processes.
Industrial Applications[edit]
Aspergillus tubingensis has significant industrial applications due to its ability to produce various enzymes. These enzymes are used in the production of food, beverages, and biofuels. The species is particularly noted for its production of proteases, amylases, and cellulases, which are utilized in the food processing and textile industries.
Medical Relevance[edit]
While Aspergillus tubingensis is primarily known for its industrial applications, it can also be a pathogen in immunocompromised individuals. It is capable of causing aspergillosis, a group of diseases that can affect the respiratory system and other organs. Proper identification and differentiation from other Aspergillus species are crucial for effective treatment.
Research and Genetic Studies[edit]
Recent studies have focused on the genetic makeup of Aspergillus tubingensis to better understand its capabilities and potential applications. The genome of A. tubingensis has been sequenced, providing insights into its metabolic pathways and enzyme production.
See Also[edit]
References[edit]
<references group="" responsive="1"></references>
External Links[edit]
Ad. Transform your life with W8MD's Budget GLP-1 injections from $75


W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Weight loss injections in NYC (generic and brand names):
- Zepbound / Mounjaro, Wegovy / Ozempic, Saxenda
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $75 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointmentsNYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
