Ascus
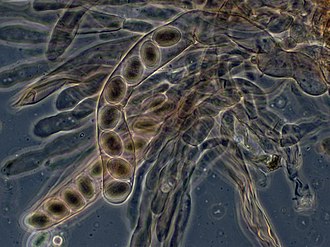


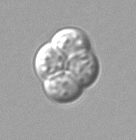

Ascus (plural: asci) is a term used in mycology to describe a specialized cell in fungi of the phylum Ascomycota that contains typically one to eight spores, called ascospores. The development and structure of the ascus are key diagnostic features in the identification and classification of fungi within the Ascomycota.
Structure and Function[edit]
The ascus is usually a elongated sac-like structure, which serves as the site of meiosis and subsequent mitosis in fungal reproduction. This process leads to the formation of ascospores, which are released to initiate a new cycle of growth when conditions are favorable. Asci can vary in shape and size, but most commonly they are cylindrical or flask-shaped. The wall of the ascus can be thin and delicate or thick and protective, depending on the species and environmental conditions.
Types of Asci[edit]
There are several types of asci, classified based on their mechanism of spore release. The most common types include: - Unitunicate operculate asci: These have a single wall layer and a lid-like structure (operculum) that opens to release the spores. - Unitunicate inoperculate asci: These also have a single wall layer but lack an operculum. Spore release occurs through a pore or by the ascus disintegrating. - Bitunicate asci: Characterized by having two wall layers, an outer elastic layer and an inner rigid layer. The expansion of the inner layer forces the ascus to stretch and eventually rupture, releasing the spores.
Ecological Role[edit]
Asci play a crucial role in the ecosystem by contributing to the decomposition of dead organic material, thus recycling nutrients back into the environment. Many ascomycete fungi are also important plant pathogens, causing diseases that can have significant economic impacts on agriculture and forestry. Conversely, some species form beneficial symbiotic relationships with plants (e.g., mycorrhizae) and lichens, which can enhance plant growth and ecosystem stability.
Economic and Medical Importance[edit]
Several species of Ascomycota are of great economic and medical importance. For example, the genus Penicillium includes species used in the production of antibiotics (e.g., penicillin) and cheese. Other species, such as Aspergillus, can be pathogenic to humans and animals, causing a range of diseases known as aspergillosis.
Research and Biotechnology[edit]
The study of asci and ascospores is important in biotechnology and genetics for understanding fungal genetics and for the development of new drugs and biocontrol agents. The ease of observing meiosis and spore formation in asci makes them excellent models for genetic studies.

Ad. Transform your life with W8MD's Budget GLP-1 injections from $75


W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Weight loss injections in NYC (generic and brand names):
- Zepbound / Mounjaro, Wegovy / Ozempic, Saxenda
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $75 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointmentsNYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian