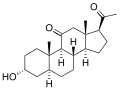
Alfaxalone
-
Chemical structure of Alfaxalone
-
Bottle of Alfaxan
-
GABAA receptor
-
Comparison of Progesterone and Alfaxalone structures
Alfaxalone[edit]
Alfaxalone is a neuroactive steroid and anesthetic agent used in veterinary medicine. It is primarily used for the induction and maintenance of anesthesia in animals. Alfaxalone is known for its rapid onset and short duration of action, making it a preferred choice in various clinical settings.
Pharmacology[edit]
Alfaxalone acts as a positive allosteric modulator of the GABA_A receptor, which is a major inhibitory neurotransmitter receptor in the central nervous system. By enhancing the effects of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), alfaxalone increases neuronal inhibition, leading to sedation and anesthesia.
The chemical structure of alfaxalone is similar to that of other neurosteroids, and it is classified as a pregnane derivative. Its lipophilic nature allows it to rapidly cross the blood-brain barrier, contributing to its quick onset of action.
Clinical Use[edit]
Alfaxalone is used in veterinary medicine for the induction and maintenance of anesthesia in a variety of animal species, including dogs, cats, and horses. It is administered intravenously, and its effects are dose-dependent. The drug is often used in combination with other anesthetic agents to achieve balanced anesthesia.
The advantages of alfaxalone include its minimal cardiovascular and respiratory depression compared to other anesthetics, such as propofol. This makes it a safer option for animals with compromised health or those undergoing minor surgical procedures.
Side Effects[edit]
While alfaxalone is generally well-tolerated, it can cause some side effects. These may include:
- Transient apnea following rapid intravenous administration.
- Mild hypotension due to vasodilation.
- Excitement or agitation during recovery, particularly if the animal is not handled in a calm environment.
Metabolism and Excretion[edit]
Alfaxalone is metabolized in the liver and excreted primarily via the kidneys. The drug's metabolites are inactive, and its elimination half-life is relatively short, contributing to its rapid recovery profile.
History[edit]
Alfaxalone was first introduced in the 1970s as part of a combination product known as "Saffan," which also contained alphadolone. However, due to adverse reactions associated with the vehicle used in Saffan, its use was limited to non-human primates and certain other species.
In the early 2000s, a new formulation of alfaxalone was developed using a cyclodextrin-based vehicle, which improved its safety profile and expanded its use in veterinary medicine.
Related Pages[edit]
Ad. Transform your life with W8MD's Budget GLP-1 injections from $75


W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Weight loss injections in NYC (generic and brand names):
- Zepbound / Mounjaro, Wegovy / Ozempic, Saxenda
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $75 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointmentsNYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian