Tooth decay: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
CSV import |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[File:Blausen 0864 ToothDecay.svg|thumb|Tooth decay]] | {{SI}} | ||
Decay of the [[teeth]] caused | {{Infobox medical condition | ||
| name = Tooth decay | |||
== | | image = [[File:Dental_Caries_Cavity_2.JPG|250px]] | ||
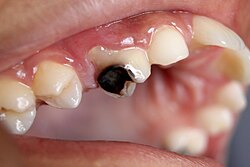
Tooth decay (dental caries) is damage to a tooth that can happen when decay-causing bacteria in your mouth make acids that attack the | | caption = A [[tooth]] with visible [[dental caries]] | ||
| field = [[Dentistry]] | |||
People of all ages can get tooth decay once they have | | synonyms = Dental caries, cavities | ||
| symptoms = [[Toothache]], visible holes in teeth, [[tooth sensitivity]] | |||
Young children are at risk for | | complications = [[Tooth loss]], [[infection]], [[abscess]] | ||
| onset = Gradual | |||
Because many older adults experience receding gums, which allows decay-causing bacteria in the mouth to come into contact with the | | duration = Long term | ||
| causes = [[Bacteria]] in the mouth, frequent snacking, sugary drinks, poor oral hygiene | |||
| risks = High sugar diet, poor oral hygiene, lack of [[fluoride]] | |||
| diagnosis = [[Dental examination]], [[X-ray]] | |||
| prevention = [[Oral hygiene]], [[fluoride]] use, regular [[dental check-up]]s | |||
| treatment = [[Fluoride treatment]], [[dental filling]], [[crown (dentistry)|crown]], [[root canal]] | |||
| frequency = Common | |||
| deaths = Rare | |||
}} | |||
[[File:Blausen 0864 ToothDecay.svg|left|thumb|Tooth decay]] | |||
Decay of the [[teeth]] caused by [[caries]], and progressing to [[cavities]] in the [[enamel]] and the [[dentine]]. | |||
== Introduction == | |||
Tooth decay (dental caries) is damage to a tooth that can happen when decay-causing bacteria in your mouth make acids that attack the tooth’s surface, or enamel. This can lead to a small hole in a tooth, called a cavity. If tooth decay is not treated, it can cause pain, infection, and even tooth loss. | |||
People of all ages can get tooth decay once they have teeth—from childhood through the senior years. | |||
Young children are at risk for '''early childhood caries,'''sometimes called baby bottle tooth decay, which is severe tooth decay in baby teeth. | |||
Because many older adults experience receding gums, which allows decay-causing bacteria in the mouth to come into contact with the tooth’s root, they can get decay on the exposed root surfaces of their teeth. | |||
Back to top | Back to top | ||
==Causes== | ==Causes== | ||
When decay-causing bacteria come into contact with sugars and starches from foods and drinks, they form an acid. This acid can attack the | When decay-causing bacteria come into contact with sugars and starches from foods and drinks, they form an acid. This acid can attack the tooth’s enamel causing it to lose minerals. | ||
This can happen if you eat or drink often, especially foods and drinks containing sugar and starches. The repeated cycles of these '''acid attacks'''will cause the enamel to continue to lose minerals. Over time, the enamel is weakened and then destroyed, forming a cavity. | |||
This can happen if you eat or drink often, especially foods and drinks containing sugar and starches. The repeated cycles of these | [[File:Tooth decay and abscess xray.png|left|thumb|X-ray of tooth decay]] | ||
[[File:Tooth decay and abscess xray.png|thumb|X-ray of tooth decay]] | |||
==Symptoms== | ==Symptoms== | ||
In early tooth decay, there are not usually any symptoms. As tooth decay advances, it can cause a toothache (tooth pain) or tooth sensitivity to sweets, hot, or cold. If the tooth becomes infected, an abscess, or pocket of pus, can form that can cause pain, facial swelling, and fever. | In early tooth decay, there are not usually any symptoms. As tooth decay advances, it can cause a toothache (tooth pain) or tooth sensitivity to sweets, hot, or cold. If the tooth becomes infected, an abscess, or pocket of pus, can form that can cause pain, facial swelling, and fever. | ||
==Diagnosis== | ==Diagnosis== | ||
Tooth decay can be found during a regular dental check-up. Early tooth decay may look like a white spot on the tooth. If the decay is more advanced, it may appear as a darker spot or a hole in the tooth. The dentist can also check the teeth for soft or sticky areas or take an x-ray, which can show decay. | Tooth decay can be found during a regular dental check-up. Early tooth decay may look like a white spot on the tooth. If the decay is more advanced, it may appear as a darker spot or a hole in the tooth. The dentist can also check the teeth for soft or sticky areas or take an x-ray, which can show decay. | ||
==Treatment== | ==Treatment== | ||
Dentists commonly treat cavities by filling them. A dentist will remove the decayed tooth tissue and then restore the tooth by filling it with a filling material. | Dentists commonly treat cavities by filling them. A dentist will remove the decayed tooth tissue and then restore the tooth by filling it with a filling material. | ||
==Helpful Tips== | ==Helpful Tips== | ||
Here are some things you can do to prevent tooth decay: | Here are some things you can do to prevent tooth decay: | ||
*Use fluoride, a mineral that can prevent tooth decay from progressing, and even reverse, or stop, early tooth decay. You can get fluoride by | *Use fluoride, a mineral that can prevent tooth decay from progressing, and even reverse, or stop, early tooth decay. You can get fluoride by | ||
**Brushing with a fluoride toothpaste. | **Brushing with a fluoride toothpaste. | ||
Revision as of 20:47, 8 April 2025

Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD medical weight loss NYC and sleep center NYC
| Tooth decay | |
|---|---|
| |
| Synonyms | Dental caries, cavities |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Toothache, visible holes in teeth, tooth sensitivity |
| Complications | Tooth loss, infection, abscess |
| Onset | Gradual |
| Duration | Long term |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Bacteria in the mouth, frequent snacking, sugary drinks, poor oral hygiene |
| Risks | High sugar diet, poor oral hygiene, lack of fluoride |
| Diagnosis | Dental examination, X-ray |
| Differential diagnosis | N/A |
| Prevention | Oral hygiene, fluoride use, regular dental check-ups |
| Treatment | Fluoride treatment, dental filling, crown, root canal |
| Medication | N/A |
| Prognosis | N/A |
| Frequency | Common |
| Deaths | Rare |

Decay of the teeth caused by caries, and progressing to cavities in the enamel and the dentine.
Introduction
Tooth decay (dental caries) is damage to a tooth that can happen when decay-causing bacteria in your mouth make acids that attack the tooth’s surface, or enamel. This can lead to a small hole in a tooth, called a cavity. If tooth decay is not treated, it can cause pain, infection, and even tooth loss. People of all ages can get tooth decay once they have teeth—from childhood through the senior years. Young children are at risk for early childhood caries,sometimes called baby bottle tooth decay, which is severe tooth decay in baby teeth. Because many older adults experience receding gums, which allows decay-causing bacteria in the mouth to come into contact with the tooth’s root, they can get decay on the exposed root surfaces of their teeth. Back to top
Causes
When decay-causing bacteria come into contact with sugars and starches from foods and drinks, they form an acid. This acid can attack the tooth’s enamel causing it to lose minerals. This can happen if you eat or drink often, especially foods and drinks containing sugar and starches. The repeated cycles of these acid attackswill cause the enamel to continue to lose minerals. Over time, the enamel is weakened and then destroyed, forming a cavity.

Symptoms
In early tooth decay, there are not usually any symptoms. As tooth decay advances, it can cause a toothache (tooth pain) or tooth sensitivity to sweets, hot, or cold. If the tooth becomes infected, an abscess, or pocket of pus, can form that can cause pain, facial swelling, and fever.
Diagnosis
Tooth decay can be found during a regular dental check-up. Early tooth decay may look like a white spot on the tooth. If the decay is more advanced, it may appear as a darker spot or a hole in the tooth. The dentist can also check the teeth for soft or sticky areas or take an x-ray, which can show decay.
Treatment
Dentists commonly treat cavities by filling them. A dentist will remove the decayed tooth tissue and then restore the tooth by filling it with a filling material.
Helpful Tips
Here are some things you can do to prevent tooth decay:
- Use fluoride, a mineral that can prevent tooth decay from progressing, and even reverse, or stop, early tooth decay. You can get fluoride by
- Brushing with a fluoride toothpaste.
- Drinking tap water with fluoride.
- Using fluoride mouth rinse.
- Have a good oral hygiene routine. Brush teeth twice a day with a fluoride toothpaste and regularly clean between teeth with floss or another interdental (between-the-teeth) cleaner.
- Make smart food choices that limit foods high in sugars and starches. Eat nutritious and balanced meals and limit snacking.
- Do not use tobacco products, including smokeless tobacco. If you currently use tobacco, consider quitting.
- See a dentist for regular check-ups and professional cleanings.


