Tinea cruris: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{SI}} | |||
{{Infobox medical condition | |||
| name = Tinea cruris | |||
| image = [[File:Tinea_cruris.jpg]] | |||
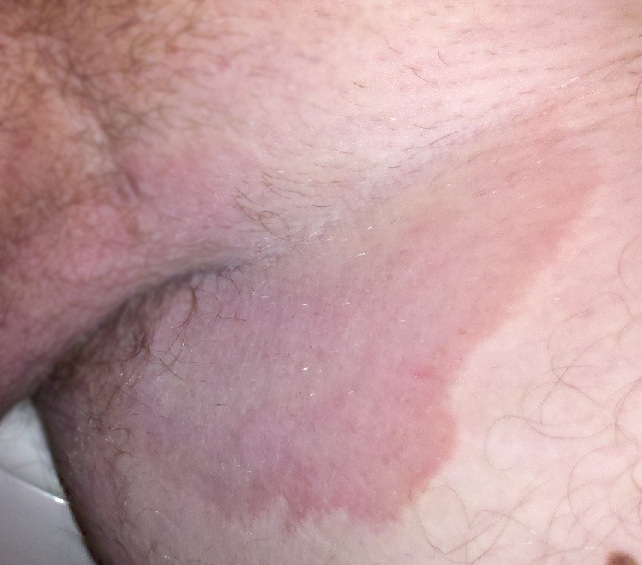
| caption = Tinea cruris affecting the groin area | |||
| synonyms = Jock itch, crotch itch, gym itch | |||
| specialty = [[Dermatology]] | |||
| symptoms = [[Itching]], [[redness]], [[rash]] in the groin area | |||
| complications = [[Secondary infection]] | |||
| onset = More common in [[adolescents]] and [[adults]] | |||
| duration = Can be [[chronic]] if untreated | |||
| causes = [[Fungal infection]] by ''[[Trichophyton]]'', ''[[Epidermophyton]]'' | |||
| risks = [[Sweating]], [[tight clothing]], [[obesity]], [[diabetes]] | |||
| diagnosis = [[Clinical examination]], [[KOH test]], [[fungal culture]] | |||
| differential = [[Intertrigo]], [[psoriasis]], [[contact dermatitis]] | |||
| prevention = Keeping the groin area dry, wearing loose-fitting clothing | |||
| treatment = [[Topical antifungal]] creams, [[oral antifungal]] medications | |||
| medication = [[Clotrimazole]], [[terbinafine]], [[miconazole]] | |||
| frequency = Common | |||
}} | |||
{{Short description|Fungal infection of the groin area}} | {{Short description|Fungal infection of the groin area}} | ||
'''Tinea cruris''', commonly known as '''jock itch''', is a [[dermatophyte]] [[fungal infection]] that affects the [[groin]] area. It is a form of [[tinea]], which is a group of diseases caused by fungi known as [[dermatophytes]]. | '''Tinea cruris''', commonly known as '''jock itch''', is a [[dermatophyte]] [[fungal infection]] that affects the [[groin]] area. It is a form of [[tinea]], which is a group of diseases caused by fungi known as [[dermatophytes]]. | ||
==Signs and symptoms== | ==Signs and symptoms== | ||
Tinea cruris typically presents as a red, itchy rash in the groin area. The rash may have a well-defined edge and can spread to the inner thighs and buttocks. The affected skin may become scaly or flaky, and in some cases, blisters may form. The itching can be intense, leading to discomfort and irritation. | Tinea cruris typically presents as a red, itchy rash in the groin area. The rash may have a well-defined edge and can spread to the inner thighs and buttocks. The affected skin may become scaly or flaky, and in some cases, blisters may form. The itching can be intense, leading to discomfort and irritation. | ||
==Causes== | ==Causes== | ||
Tinea cruris is caused by [[dermatophyte]] fungi, most commonly ''[[Trichophyton rubrum]]''. These fungi thrive in warm, moist environments, making the groin area particularly susceptible. Factors that increase the risk of developing tinea cruris include excessive sweating, wearing tight clothing, and having a weakened [[immune system]]. | Tinea cruris is caused by [[dermatophyte]] fungi, most commonly ''[[Trichophyton rubrum]]''. These fungi thrive in warm, moist environments, making the groin area particularly susceptible. Factors that increase the risk of developing tinea cruris include excessive sweating, wearing tight clothing, and having a weakened [[immune system]]. | ||
==Diagnosis== | ==Diagnosis== | ||
Diagnosis of tinea cruris is typically based on the appearance of the rash and the patient's history. A [[skin scraping]] may be taken and examined under a microscope to confirm the presence of fungal elements. In some cases, a [[culture]] may be performed to identify the specific type of fungus. | Diagnosis of tinea cruris is typically based on the appearance of the rash and the patient's history. A [[skin scraping]] may be taken and examined under a microscope to confirm the presence of fungal elements. In some cases, a [[culture]] may be performed to identify the specific type of fungus. | ||
==Treatment== | ==Treatment== | ||
Treatment for tinea cruris involves the use of topical [[antifungal]] medications, such as [[clotrimazole]], [[miconazole]], or [[terbinafine]]. In more severe cases, oral antifungal medications may be prescribed. It is important to keep the affected area clean and dry, and to avoid tight-fitting clothing to prevent further irritation. | Treatment for tinea cruris involves the use of topical [[antifungal]] medications, such as [[clotrimazole]], [[miconazole]], or [[terbinafine]]. In more severe cases, oral antifungal medications may be prescribed. It is important to keep the affected area clean and dry, and to avoid tight-fitting clothing to prevent further irritation. | ||
==Prevention== | ==Prevention== | ||
Preventive measures for tinea cruris include maintaining good personal hygiene, keeping the groin area dry, and wearing loose-fitting clothing. It is also advisable to avoid sharing personal items such as towels and to change out of wet clothing promptly after exercising. | Preventive measures for tinea cruris include maintaining good personal hygiene, keeping the groin area dry, and wearing loose-fitting clothing. It is also advisable to avoid sharing personal items such as towels and to change out of wet clothing promptly after exercising. | ||
==See also== | |||
== | |||
* [[Tinea pedis]] | * [[Tinea pedis]] | ||
* [[Tinea corporis]] | * [[Tinea corporis]] | ||
* [[Dermatophyte]] | * [[Dermatophyte]] | ||
* [[Antifungal]] | * [[Antifungal]] | ||
[[Category:Fungal diseases]] | [[Category:Fungal diseases]] | ||
[[Category:Skin conditions]] | [[Category:Skin conditions]] | ||
Latest revision as of 15:58, 8 April 2025

Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD medical weight loss NYC and sleep center NYC
| Tinea cruris | |
|---|---|
| |
| Synonyms | Jock itch, crotch itch, gym itch |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | Dermatology |
| Symptoms | Itching, redness, rash in the groin area |
| Complications | Secondary infection |
| Onset | More common in adolescents and adults |
| Duration | Can be chronic if untreated |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Fungal infection by Trichophyton, Epidermophyton |
| Risks | Sweating, tight clothing, obesity, diabetes |
| Diagnosis | Clinical examination, KOH test, fungal culture |
| Differential diagnosis | Intertrigo, psoriasis, contact dermatitis |
| Prevention | Keeping the groin area dry, wearing loose-fitting clothing |
| Treatment | Topical antifungal creams, oral antifungal medications |
| Medication | Clotrimazole, terbinafine, miconazole |
| Prognosis | N/A |
| Frequency | Common |
| Deaths | N/A |
Fungal infection of the groin area
Tinea cruris, commonly known as jock itch, is a dermatophyte fungal infection that affects the groin area. It is a form of tinea, which is a group of diseases caused by fungi known as dermatophytes.
Signs and symptoms[edit]
Tinea cruris typically presents as a red, itchy rash in the groin area. The rash may have a well-defined edge and can spread to the inner thighs and buttocks. The affected skin may become scaly or flaky, and in some cases, blisters may form. The itching can be intense, leading to discomfort and irritation.
Causes[edit]
Tinea cruris is caused by dermatophyte fungi, most commonly Trichophyton rubrum. These fungi thrive in warm, moist environments, making the groin area particularly susceptible. Factors that increase the risk of developing tinea cruris include excessive sweating, wearing tight clothing, and having a weakened immune system.
Diagnosis[edit]
Diagnosis of tinea cruris is typically based on the appearance of the rash and the patient's history. A skin scraping may be taken and examined under a microscope to confirm the presence of fungal elements. In some cases, a culture may be performed to identify the specific type of fungus.
Treatment[edit]
Treatment for tinea cruris involves the use of topical antifungal medications, such as clotrimazole, miconazole, or terbinafine. In more severe cases, oral antifungal medications may be prescribed. It is important to keep the affected area clean and dry, and to avoid tight-fitting clothing to prevent further irritation.
Prevention[edit]
Preventive measures for tinea cruris include maintaining good personal hygiene, keeping the groin area dry, and wearing loose-fitting clothing. It is also advisable to avoid sharing personal items such as towels and to change out of wet clothing promptly after exercising.