Pneumocystis pneumonia: Difference between revisions
mNo edit summary |
CSV import |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
'''Pneumocystis pneumonia''' (also known as '''PCP''') is a form of [[pneumonia]], an inflammatory condition of the [[lung]] affecting primarily the microscopic air sacs known as [[alveoli]], that is caused by the yeast-like fungus ''[[Pneumocystis jirovecii]]''. | {{SI}} | ||
{{Infobox medical condition | |||
| name = Pneumocystis pneumonia | |||
| image = [[File:Pneumocystis.jpg|alt=Micrograph of Pneumocystis jirovecii in lung tissue]] | |||
| caption = Micrograph of ''[[Pneumocystis jirovecii]]'' in lung tissue | |||
| field = [[Infectious disease]] | |||
| synonyms = PCP, Pneumocystosis | |||
| symptoms = [[Cough]], [[fever]], [[shortness of breath]], [[chest pain]] | |||
| complications = [[Respiratory failure]], [[pneumothorax]] | |||
| onset = Gradual | |||
| duration = Weeks to months | |||
| causes = ''[[Pneumocystis jirovecii]]'' | |||
| risks = [[HIV/AIDS]], [[immunosuppressive therapy]], [[organ transplantation]] | |||
| diagnosis = [[Chest X-ray]], [[CT scan]], [[sputum culture]], [[bronchoalveolar lavage]] | |||
| differential = [[Bacterial pneumonia]], [[tuberculosis]], [[fungal infections]] | |||
| prevention = [[Prophylactic antibiotics]] (e.g., [[trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole]]) | |||
| treatment = [[Antibiotics]] (e.g., [[trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole]], [[pentamidine]]) | |||
| medication = [[Corticosteroids]] for severe cases | |||
| prognosis = Variable, depends on underlying conditions | |||
| frequency = Common in [[HIV/AIDS]] patients | |||
| deaths = Significant if untreated | |||
}} | |||
'''Pneumocystis pneumonia''' (also known as '''PCP''') is a form of [[pneumonia]], an inflammatory condition of the [[lung]] affecting primarily the microscopic air sacs known as [[alveoli]], that is caused by the yeast-like fungus ''[[Pneumocystis jirovecii]]''. | |||
[[File:CT of bilateral pneumothoraces by pneumocystis pneumonia cysts.jpg|CT of bilateral pneumothoraces by pneumocystis pneumonia cysts]] | [[File:CT of bilateral pneumothoraces by pneumocystis pneumonia cysts.jpg|CT of bilateral pneumothoraces by pneumocystis pneumonia cysts]] | ||
== Signs and symptoms == | == Signs and symptoms == | ||
The most common symptoms of PCP are [[cough]], [[fever]], and difficulty breathing. Other symptoms can include [[chills]], [[night sweats]], [[chest pain]], and [[fatigue]]. | The most common symptoms of PCP are [[cough]], [[fever]], and difficulty breathing. Other symptoms can include [[chills]], [[night sweats]], [[chest pain]], and [[fatigue]]. | ||
<youtube> | <youtube> | ||
title='''{{PAGENAME}}''' | title='''{{PAGENAME}}''' | ||
movie_url=http://www.youtube.com/v/-sM-sRGtOcE | movie_url=http://www.youtube.com/v/-sM-sRGtOcE | ||
&rel=1 | &rel=1 | ||
| Line 16: | Line 35: | ||
height=600 | height=600 | ||
</youtube> | </youtube> | ||
== Cause == | == Cause == | ||
PCP is caused by the yeast-like fungus ''Pneumocystis jirovecii''. It is not known exactly how this organism is spread, but it is believed to be airborne. | PCP is caused by the yeast-like fungus ''Pneumocystis jirovecii''. It is not known exactly how this organism is spread, but it is believed to be airborne. | ||
== Diagnosis == | == Diagnosis == | ||
Diagnosis of PCP can be challenging, as the symptoms are similar to those of other forms of pneumonia. The diagnosis is usually confirmed by identifying ''Pneumocystis jirovecii'' in a sample of lung tissue or fluid. | Diagnosis of PCP can be challenging, as the symptoms are similar to those of other forms of pneumonia. The diagnosis is usually confirmed by identifying ''Pneumocystis jirovecii'' in a sample of lung tissue or fluid. | ||
== Treatment == | == Treatment == | ||
Treatment for PCP typically involves a combination of [[antibiotics]] and [[corticosteroids]]. The specific medications used may vary depending on the severity of the infection and the patient's overall health. | Treatment for PCP typically involves a combination of [[antibiotics]] and [[corticosteroids]]. The specific medications used may vary depending on the severity of the infection and the patient's overall health. | ||
== Prognosis == | == Prognosis == | ||
With treatment, most people with PCP can recover. However, the condition can be life-threatening, particularly in those with weakened immune systems. | With treatment, most people with PCP can recover. However, the condition can be life-threatening, particularly in those with weakened immune systems. | ||
== Prevention == | == Prevention == | ||
Prevention of PCP involves taking steps to avoid exposure to ''Pneumocystis jirovecii'' and to strengthen the immune system. | Prevention of PCP involves taking steps to avoid exposure to ''Pneumocystis jirovecii'' and to strengthen the immune system. | ||
== See also == | == See also == | ||
* [[Pneumonia]] | * [[Pneumonia]] | ||
| Line 37: | Line 50: | ||
* [[Antibiotics]] | * [[Antibiotics]] | ||
* [[Corticosteroids]] | * [[Corticosteroids]] | ||
[[Category:Infectious diseases]] | [[Category:Infectious diseases]] | ||
[[Category:Pneumonia]] | [[Category:Pneumonia]] | ||
[[Category:Fungal diseases]] | [[Category:Fungal diseases]] | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
Latest revision as of 15:41, 8 April 2025

Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD medical weight loss NYC and sleep center NYC
| Pneumocystis pneumonia | |
|---|---|

| |
| Synonyms | PCP, Pneumocystosis |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Cough, fever, shortness of breath, chest pain |
| Complications | Respiratory failure, pneumothorax |
| Onset | Gradual |
| Duration | Weeks to months |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Pneumocystis jirovecii |
| Risks | HIV/AIDS, immunosuppressive therapy, organ transplantation |
| Diagnosis | Chest X-ray, CT scan, sputum culture, bronchoalveolar lavage |
| Differential diagnosis | Bacterial pneumonia, tuberculosis, fungal infections |
| Prevention | Prophylactic antibiotics (e.g., trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole) |
| Treatment | Antibiotics (e.g., trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole, pentamidine) |
| Medication | Corticosteroids for severe cases |
| Prognosis | Variable, depends on underlying conditions |
| Frequency | Common in HIV/AIDS patients |
| Deaths | Significant if untreated |
Pneumocystis pneumonia (also known as PCP) is a form of pneumonia, an inflammatory condition of the lung affecting primarily the microscopic air sacs known as alveoli, that is caused by the yeast-like fungus Pneumocystis jirovecii.
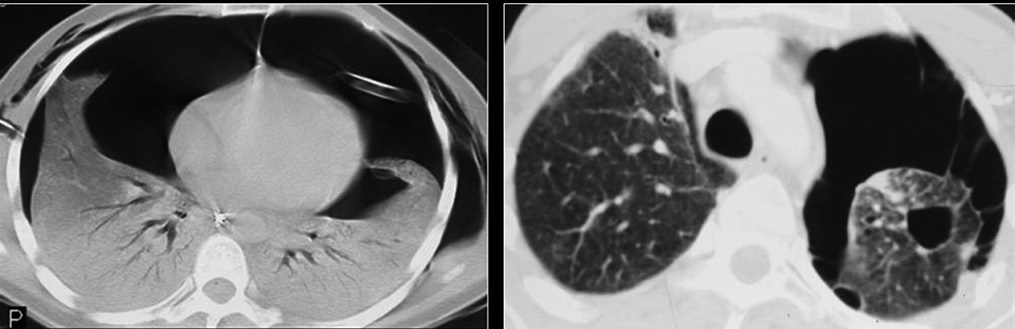
Signs and symptoms[edit]
The most common symptoms of PCP are cough, fever, and difficulty breathing. Other symptoms can include chills, night sweats, chest pain, and fatigue.
Cause[edit]
PCP is caused by the yeast-like fungus Pneumocystis jirovecii. It is not known exactly how this organism is spread, but it is believed to be airborne.
Diagnosis[edit]
Diagnosis of PCP can be challenging, as the symptoms are similar to those of other forms of pneumonia. The diagnosis is usually confirmed by identifying Pneumocystis jirovecii in a sample of lung tissue or fluid.
Treatment[edit]
Treatment for PCP typically involves a combination of antibiotics and corticosteroids. The specific medications used may vary depending on the severity of the infection and the patient's overall health.
Prognosis[edit]
With treatment, most people with PCP can recover. However, the condition can be life-threatening, particularly in those with weakened immune systems.
Prevention[edit]
Prevention of PCP involves taking steps to avoid exposure to Pneumocystis jirovecii and to strengthen the immune system.


