Posterior ramus syndrome: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{SI}} | |||
{{Infobox medical condition | |||
| name = Posterior ramus syndrome | |||
| image = [[File:Spinal_nerve.svg|250px]] | |||
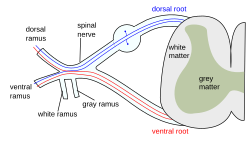
| caption = Diagram of a [[spinal nerve]], showing the posterior ramus | |||
| synonyms = [[Thoracolumbar junction syndrome]], [[Maigne syndrome]] | |||
| specialty = [[Orthopedics]], [[Neurology]] | |||
| symptoms = [[Lower back pain]], [[buttock pain]], [[groin pain]] | |||
| onset = Often [[adult]] | |||
| duration = [[Chronic]] | |||
| causes = [[Facet joint dysfunction]], [[nerve irritation]] | |||
| risks = [[Poor posture]], [[repetitive strain]] | |||
| diagnosis = [[Clinical examination]], [[imaging studies]] | |||
| differential = [[Sciatica]], [[hip joint disorders]], [[sacroiliac joint dysfunction]] | |||
| treatment = [[Physical therapy]], [[medication]], [[injections]] | |||
| prognosis = [[Variable]], often [[manageable]] with treatment | |||
| frequency = [[Common]] | |||
}} | |||
{{DISPLAYTITLE:Posterior Ramus Syndrome}} | {{DISPLAYTITLE:Posterior Ramus Syndrome}} | ||
'''Posterior Ramus Syndrome''', also known as '''dorsal ramus syndrome''', is a condition characterized by pain and dysfunction associated with the [[posterior ramus]] of a [[spinal nerve]]. The posterior ramus is responsible for innervating the deep muscles and skin of the back. | '''Posterior Ramus Syndrome''', also known as '''dorsal ramus syndrome''', is a condition characterized by pain and dysfunction associated with the [[posterior ramus]] of a [[spinal nerve]]. The posterior ramus is responsible for innervating the deep muscles and skin of the back. | ||
== Anatomy == | == Anatomy == | ||
The [[spinal nerve]] is a mixed nerve that emerges from the [[spinal cord]]. It divides into two primary branches: the [[anterior ramus]] and the posterior ramus. The posterior ramus innervates the [[erector spinae]] muscles and the [[facet joints]] of the spine. | The [[spinal nerve]] is a mixed nerve that emerges from the [[spinal cord]]. It divides into two primary branches: the [[anterior ramus]] and the posterior ramus. The posterior ramus innervates the [[erector spinae]] muscles and the [[facet joints]] of the spine. | ||
== Pathophysiology == | == Pathophysiology == | ||
Posterior Ramus Syndrome occurs when there is irritation or injury to the posterior ramus. This can result from [[trauma]], [[degenerative disc disease]], or [[facet joint arthritis]]. The condition leads to localized pain, muscle spasm, and sometimes referred pain patterns. | Posterior Ramus Syndrome occurs when there is irritation or injury to the posterior ramus. This can result from [[trauma]], [[degenerative disc disease]], or [[facet joint arthritis]]. The condition leads to localized pain, muscle spasm, and sometimes referred pain patterns. | ||
== Clinical Presentation == | == Clinical Presentation == | ||
Patients with Posterior Ramus Syndrome typically present with: | Patients with Posterior Ramus Syndrome typically present with: | ||
| Line 17: | Line 29: | ||
* Reduced range of motion | * Reduced range of motion | ||
* Pain that may radiate to the [[buttocks]] or [[thighs]] | * Pain that may radiate to the [[buttocks]] or [[thighs]] | ||
== Diagnosis == | == Diagnosis == | ||
Diagnosis is primarily clinical, based on the patient's history and physical examination. Imaging studies such as [[MRI]] or [[CT scan]] may be used to rule out other conditions. Diagnostic [[nerve block]]s can confirm the involvement of the posterior ramus. | Diagnosis is primarily clinical, based on the patient's history and physical examination. Imaging studies such as [[MRI]] or [[CT scan]] may be used to rule out other conditions. Diagnostic [[nerve block]]s can confirm the involvement of the posterior ramus. | ||
== Treatment == | == Treatment == | ||
Treatment options include: | Treatment options include: | ||
| Line 27: | Line 37: | ||
* [[Corticosteroid injections]] | * [[Corticosteroid injections]] | ||
* [[Radiofrequency ablation]] | * [[Radiofrequency ablation]] | ||
== Prognosis == | == Prognosis == | ||
With appropriate treatment, many patients experience significant relief of symptoms. However, chronic cases may require ongoing management. | With appropriate treatment, many patients experience significant relief of symptoms. However, chronic cases may require ongoing management. | ||
== See also == | |||
== | |||
* [[Spinal nerve]] | * [[Spinal nerve]] | ||
* [[Facet joint]] | * [[Facet joint]] | ||
* [[Back pain]] | * [[Back pain]] | ||
[[Category:Musculoskeletal disorders]] | [[Category:Musculoskeletal disorders]] | ||
Latest revision as of 15:34, 8 April 2025

Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD medical weight loss NYC and sleep center NYC
| Posterior ramus syndrome | |
|---|---|
| |
| Synonyms | Thoracolumbar junction syndrome, Maigne syndrome |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | Orthopedics, Neurology |
| Symptoms | Lower back pain, buttock pain, groin pain |
| Complications | N/A |
| Onset | Often adult |
| Duration | Chronic |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Facet joint dysfunction, nerve irritation |
| Risks | Poor posture, repetitive strain |
| Diagnosis | Clinical examination, imaging studies |
| Differential diagnosis | Sciatica, hip joint disorders, sacroiliac joint dysfunction |
| Prevention | N/A |
| Treatment | Physical therapy, medication, injections |
| Medication | N/A |
| Prognosis | Variable, often manageable with treatment |
| Frequency | Common |
| Deaths | N/A |
Posterior Ramus Syndrome, also known as dorsal ramus syndrome, is a condition characterized by pain and dysfunction associated with the posterior ramus of a spinal nerve. The posterior ramus is responsible for innervating the deep muscles and skin of the back.
Anatomy[edit]
The spinal nerve is a mixed nerve that emerges from the spinal cord. It divides into two primary branches: the anterior ramus and the posterior ramus. The posterior ramus innervates the erector spinae muscles and the facet joints of the spine.
Pathophysiology[edit]
Posterior Ramus Syndrome occurs when there is irritation or injury to the posterior ramus. This can result from trauma, degenerative disc disease, or facet joint arthritis. The condition leads to localized pain, muscle spasm, and sometimes referred pain patterns.
Clinical Presentation[edit]
Patients with Posterior Ramus Syndrome typically present with:
- Localized back pain
- Muscle tenderness
- Reduced range of motion
- Pain that may radiate to the buttocks or thighs
Diagnosis[edit]
Diagnosis is primarily clinical, based on the patient's history and physical examination. Imaging studies such as MRI or CT scan may be used to rule out other conditions. Diagnostic nerve blocks can confirm the involvement of the posterior ramus.
Treatment[edit]
Treatment options include:
- Physical therapy
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
- Corticosteroid injections
- Radiofrequency ablation
Prognosis[edit]
With appropriate treatment, many patients experience significant relief of symptoms. However, chronic cases may require ongoing management.