Acetabular fracture: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Infobox medical condition | |||
| name = Acetabular fracture | |||
| image = [[File:AcetabularfracX.png|250px]] | |||
| caption = X-ray of an acetabular fracture | |||
| field = [[Orthopedic surgery]] | |||
| symptoms = [[Hip pain]], [[inability to bear weight]], [[limb shortening]] | |||
| complications = [[Post-traumatic arthritis]], [[avascular necrosis]], [[nerve injury]] | |||
| onset = Sudden, due to [[trauma]] | |||
| duration = Varies, depending on severity and treatment | |||
| causes = [[High-energy trauma]], [[falls]], [[motor vehicle accidents]] | |||
| risks = [[Osteoporosis]], [[high-impact sports]] | |||
| diagnosis = [[X-ray]], [[CT scan]] | |||
| differential = [[Hip dislocation]], [[femoral neck fracture]] | |||
| treatment = [[Surgical fixation]], [[traction]], [[physical therapy]] | |||
| prognosis = Depends on severity and treatment; risk of [[arthritis]] | |||
| frequency = Rare, more common in [[young adults]] | |||
}} | |||
{{Short description|A comprehensive overview of acetabular fractures}} | {{Short description|A comprehensive overview of acetabular fractures}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:Acet_anatomy_bone_model1.jpg|Acet_anatomy_bone_model1 | |||
File:Acet_anatomy_bone_model_obturator_view3.jpg|Acet_anatomy_bone_model_obturator_view3 | |||
File:Acet_anatomy_bone_model2.jpg|Acet_anatomy_bone_model2 | |||
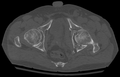
File:Acetabular_Fracture_CT.png|Acetabular_Fracture_CT | |||
File:AcetabFracSagMark.png|AcetabFracSagMark | |||
File:Acet_-_Post_wall_01.jpg|Acet_-_Post_wall_01 | |||
File:Acet_-_Post_wall_02.jpg|Acet_-_Post_wall_02 | |||
File:Acet_-_Post_wall_03.jpg|Acet_-_Post_wall_03 | |||
File:Acet_Ant_wall_Cooper_1.jpg|Acet_Ant_wall_Cooper_1 | |||
File:Acet_Ant_wall_CT.jpg|Acet_Ant_wall_CT | |||
File:Acet_Ant.wall_post_op.jpg|Acet_Ant.wall_post_op | |||
File:Acet_High_Ant_Column_01.jpg|Acet_High_Ant_Column_01 | |||
</gallery> | |||
==Acetabular Fracture== | ==Acetabular Fracture== | ||
| Line 15: | Line 46: | ||
==Mechanism of Injury== | ==Mechanism of Injury== | ||
Acetabular fractures typically occur due to high-energy impacts. Common mechanisms include: | Acetabular fractures typically occur due to high-energy impacts. Common mechanisms include: | ||
* [[Motor vehicle collisions]] | * [[Motor vehicle collisions]] | ||
* Falls from a height | * Falls from a height | ||
* Direct trauma to the hip region | * Direct trauma to the hip region | ||
The direction and magnitude of the force, as well as the position of the femur at the time of impact, influence the fracture pattern. | The direction and magnitude of the force, as well as the position of the femur at the time of impact, influence the fracture pattern. | ||
==Clinical Presentation== | ==Clinical Presentation== | ||
Patients with acetabular fractures often present with: | Patients with acetabular fractures often present with: | ||
* Severe pain in the hip or groin | * Severe pain in the hip or groin | ||
* Inability to bear weight on the affected leg | * Inability to bear weight on the affected leg | ||
| Line 32: | Line 60: | ||
==Diagnosis== | ==Diagnosis== | ||
Diagnosis of acetabular fractures involves a combination of clinical examination and imaging studies. Key diagnostic tools include: | Diagnosis of acetabular fractures involves a combination of clinical examination and imaging studies. Key diagnostic tools include: | ||
* [[X-ray]]: Initial imaging to assess the fracture pattern and any associated dislocations. | * [[X-ray]]: Initial imaging to assess the fracture pattern and any associated dislocations. | ||
* [[CT scan]]: Provides detailed information about the fracture configuration and is essential for surgical planning. | * [[CT scan]]: Provides detailed information about the fracture configuration and is essential for surgical planning. | ||
| Line 38: | Line 65: | ||
==Treatment== | ==Treatment== | ||
The treatment of acetabular fractures depends on the type and severity of the fracture, as well as the patient's overall health and activity level. Treatment options include: | The treatment of acetabular fractures depends on the type and severity of the fracture, as well as the patient's overall health and activity level. Treatment options include: | ||
* '''Non-surgical management''': Indicated for non-displaced fractures or patients who are not surgical candidates. This includes bed rest, traction, and physical therapy. | * '''Non-surgical management''': Indicated for non-displaced fractures or patients who are not surgical candidates. This includes bed rest, traction, and physical therapy. | ||
* '''Surgical management''': Required for displaced fractures to restore joint congruity and stability. Surgical options include open reduction and internal fixation (ORIF). | * '''Surgical management''': Required for displaced fractures to restore joint congruity and stability. Surgical options include open reduction and internal fixation (ORIF). | ||
| Line 44: | Line 70: | ||
==Complications== | ==Complications== | ||
Potential complications of acetabular fractures include: | Potential complications of acetabular fractures include: | ||
* [[Post-traumatic arthritis]] | * [[Post-traumatic arthritis]] | ||
* [[Avascular necrosis]] of the femoral head | * [[Avascular necrosis]] of the femoral head | ||
| Line 57: | Line 82: | ||
* [[Hip dislocation]] | * [[Hip dislocation]] | ||
* [[Orthopedic surgery]] | * [[Orthopedic surgery]] | ||
[[Category:Orthopedic surgery]] | [[Category:Orthopedic surgery]] | ||
[[Category:Traumatology]] | [[Category:Traumatology]] | ||
[[Category:Fractures]] | [[Category:Fractures]] | ||
Latest revision as of 04:55, 8 April 2025
| Acetabular fracture | |
|---|---|

| |
| Synonyms | N/A |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Hip pain, inability to bear weight, limb shortening |
| Complications | Post-traumatic arthritis, avascular necrosis, nerve injury |
| Onset | Sudden, due to trauma |
| Duration | Varies, depending on severity and treatment |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | High-energy trauma, falls, motor vehicle accidents |
| Risks | Osteoporosis, high-impact sports |
| Diagnosis | X-ray, CT scan |
| Differential diagnosis | Hip dislocation, femoral neck fracture |
| Prevention | N/A |
| Treatment | Surgical fixation, traction, physical therapy |
| Medication | N/A |
| Prognosis | Depends on severity and treatment; risk of arthritis |
| Frequency | Rare, more common in young adults |
| Deaths | N/A |
A comprehensive overview of acetabular fractures
-
Acet_anatomy_bone_model1
-
Acet_anatomy_bone_model_obturator_view3
-
Acet_anatomy_bone_model2
-
Acetabular_Fracture_CT
-
AcetabFracSagMark
-
Acet_-_Post_wall_01
-
Acet_-_Post_wall_02
-
Acet_-_Post_wall_03
-
Acet_Ant_wall_Cooper_1
-
Acet_Ant_wall_CT
-
Acet_Ant.wall_post_op
-
Acet_High_Ant_Column_01
Acetabular Fracture[edit]
An acetabular fracture is a break in the acetabulum, the concave surface of the pelvis that articulates with the femoral head to form the hip joint. These fractures are often the result of high-energy trauma, such as motor vehicle accidents or falls from significant heights, and can be associated with other injuries.
Anatomy[edit]
The acetabulum is a deep, cup-shaped structure that forms the socket of the hip joint. It is composed of three bones: the ilium, ischium, and pubis, which converge at the acetabulum. The acetabular surface is covered with articular cartilage, which facilitates smooth movement of the femoral head.
Classification[edit]
Acetabular fractures are classified based on the location and pattern of the fracture. The most widely used classification system is the Letournel and Judet classification, which divides acetabular fractures into two main types:
- Elementary fractures: These include simple fracture patterns such as posterior wall, anterior wall, posterior column, anterior column, and transverse fractures.
- Associated fractures: These involve more complex patterns, such as T-shaped fractures, both column fractures, and anterior column with posterior hemitransverse fractures.
Mechanism of Injury[edit]
Acetabular fractures typically occur due to high-energy impacts. Common mechanisms include:
- Motor vehicle collisions
- Falls from a height
- Direct trauma to the hip region
The direction and magnitude of the force, as well as the position of the femur at the time of impact, influence the fracture pattern.
Clinical Presentation[edit]
Patients with acetabular fractures often present with:
- Severe pain in the hip or groin
- Inability to bear weight on the affected leg
- Deformity or swelling in the hip region
- Possible associated injuries, such as femoral head dislocation or sciatic nerve injury
Diagnosis[edit]
Diagnosis of acetabular fractures involves a combination of clinical examination and imaging studies. Key diagnostic tools include:
- X-ray: Initial imaging to assess the fracture pattern and any associated dislocations.
- CT scan: Provides detailed information about the fracture configuration and is essential for surgical planning.
Treatment[edit]
The treatment of acetabular fractures depends on the type and severity of the fracture, as well as the patient's overall health and activity level. Treatment options include:
- Non-surgical management: Indicated for non-displaced fractures or patients who are not surgical candidates. This includes bed rest, traction, and physical therapy.
- Surgical management: Required for displaced fractures to restore joint congruity and stability. Surgical options include open reduction and internal fixation (ORIF).
Complications[edit]
Potential complications of acetabular fractures include:
- Post-traumatic arthritis
- Avascular necrosis of the femoral head
- Heterotopic ossification
- Nerve injury, particularly to the sciatic nerve
Prognosis[edit]
The prognosis for acetabular fractures varies based on the severity of the fracture and the success of the treatment. Early and appropriate management is crucial to minimize complications and improve functional outcomes.