Knee dislocation: Difference between revisions
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
CSV import |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[ | {{SI}} | ||
{{Infobox medical condition | |||
| name = Knee dislocation | |||
| image = [[File:PosteriorKneeDIsclocation.jpg|250px]] | |||
| caption = Posterior knee dislocation | |||
| field = [[Orthopedics]] | |||
| symptoms = [[Pain]], [[swelling]], [[instability]] of the knee | |||
| complications = [[Vascular injury]], [[nerve injury]], [[compartment syndrome]] | |||
| onset = Sudden, often due to [[trauma]] | |||
| duration = Varies, depending on severity and treatment | |||
| causes = [[High-energy trauma]], [[sports injuries]], [[falls]] | |||
| risks = [[Obesity]], [[previous knee injuries]] | |||
| diagnosis = [[Physical examination]], [[X-ray]], [[MRI]] | |||
| differential = [[Knee sprain]], [[knee fracture]], [[patellar dislocation]] | |||
| prevention = [[Protective gear]], [[strength training]] | |||
| treatment = [[Reduction (orthopedic)]], [[surgery]], [[physical therapy]] | |||
| prognosis = Varies, potential for [[chronic pain]] and [[arthritis]] | |||
| frequency = Rare | |||
}} | |||
[[file:CTAngioOcclusionRtPop.jpg|left|thumb]] [[file:SegondFracture.JPG|left|thumb]] [[file:Lateral-knee-dislocation-1.jpg|left|thumb]] '''Knee dislocation''' | |||
A '''knee dislocation''' is a severe injury that occurs when the bones that form the knee joint are out of place. This condition is different from a [[patellar dislocation]], which involves the displacement of the kneecap. Knee dislocations are often the result of high-energy trauma, such as car accidents or sports injuries. | A '''knee dislocation''' is a severe injury that occurs when the bones that form the knee joint are out of place. This condition is different from a [[patellar dislocation]], which involves the displacement of the kneecap. Knee dislocations are often the result of high-energy trauma, such as car accidents or sports injuries. | ||
==Anatomy of the Knee== | ==Anatomy of the Knee== | ||
The knee joint is composed of three bones: the [[femur]] (thigh bone), the [[tibia]] (shin bone), and the [[patella]] (kneecap). These bones are connected by a complex network of [[ligaments]], including the [[anterior cruciate ligament]] (ACL), [[posterior cruciate ligament]] (PCL), [[medial collateral ligament]] (MCL), and [[lateral collateral ligament]] (LCL). The knee also contains [[cartilage]] and [[menisci]] that cushion the joint and facilitate smooth movement. | The knee joint is composed of three bones: the [[femur]] (thigh bone), the [[tibia]] (shin bone), and the [[patella]] (kneecap). These bones are connected by a complex network of [[ligaments]], including the [[anterior cruciate ligament]] (ACL), [[posterior cruciate ligament]] (PCL), [[medial collateral ligament]] (MCL), and [[lateral collateral ligament]] (LCL). The knee also contains [[cartilage]] and [[menisci]] that cushion the joint and facilitate smooth movement. | ||
==Causes== | ==Causes== | ||
Knee dislocations are typically caused by high-impact trauma. Common causes include: | Knee dislocations are typically caused by high-impact trauma. Common causes include: | ||
| Line 12: | Line 28: | ||
* Falls from significant heights | * Falls from significant heights | ||
* Industrial accidents | * Industrial accidents | ||
==Symptoms== | ==Symptoms== | ||
Symptoms of a knee dislocation may include: | Symptoms of a knee dislocation may include: | ||
| Line 20: | Line 35: | ||
* Inability to move the knee | * Inability to move the knee | ||
* Numbness or tingling if nerves are affected | * Numbness or tingling if nerves are affected | ||
==Diagnosis== | ==Diagnosis== | ||
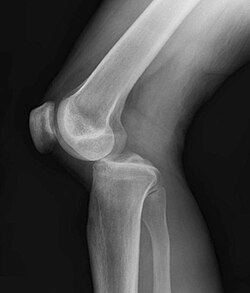
Diagnosis of a knee dislocation is usually made through a combination of physical examination and imaging studies. [[X-rays]] and [[MRI]] scans are commonly used to assess the extent of the injury and to check for associated damage to ligaments, blood vessels, and nerves. | Diagnosis of a knee dislocation is usually made through a combination of physical examination and imaging studies. [[X-rays]] and [[MRI]] scans are commonly used to assess the extent of the injury and to check for associated damage to ligaments, blood vessels, and nerves. | ||
==Treatment== | ==Treatment== | ||
Treatment for a knee dislocation often involves: | Treatment for a knee dislocation often involves: | ||
| Line 30: | Line 43: | ||
* Surgery to repair damaged ligaments, blood vessels, or nerves | * Surgery to repair damaged ligaments, blood vessels, or nerves | ||
* Physical therapy to restore function and strength | * Physical therapy to restore function and strength | ||
==Complications== | ==Complications== | ||
Complications from knee dislocations can be severe and may include: | Complications from knee dislocations can be severe and may include: | ||
| Line 37: | Line 49: | ||
* [[Chronic instability]]: Persistent instability of the knee joint may occur if ligaments do not heal properly. | * [[Chronic instability]]: Persistent instability of the knee joint may occur if ligaments do not heal properly. | ||
* [[Arthritis]]: Post-traumatic arthritis can develop in the affected knee joint over time. | * [[Arthritis]]: Post-traumatic arthritis can develop in the affected knee joint over time. | ||
==Prognosis== | ==Prognosis== | ||
The prognosis for a knee dislocation depends on the severity of the injury and the promptness of treatment. Early and appropriate management can lead to good functional outcomes, although some patients may experience long-term complications. | The prognosis for a knee dislocation depends on the severity of the injury and the promptness of treatment. Early and appropriate management can lead to good functional outcomes, although some patients may experience long-term complications. | ||
==See also== | ==See also== | ||
* [[Knee injuries]] | * [[Knee injuries]] | ||
* [[Ligament injuries]] | * [[Ligament injuries]] | ||
* [[Orthopedic surgery]] | * [[Orthopedic surgery]] | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
{{Reflist}} | {{Reflist}} | ||
==External links== | ==External links== | ||
{{Commons category|Knee dislocation}} | {{Commons category|Knee dislocation}} | ||
[[Category:Orthopedic surgery]] | [[Category:Orthopedic surgery]] | ||
[[Category:Knee injuries]] | [[Category:Knee injuries]] | ||
[[Category:Traumatology]] | [[Category:Traumatology]] | ||
{{medicine-stub}} | {{medicine-stub}} | ||
Revision as of 01:27, 8 April 2025

Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD's medical weight loss NYC, sleep center NYC
Philadelphia medical weight loss and Philadelphia sleep clinics
| Knee dislocation | |
|---|---|
| |
| Synonyms | N/A |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Pain, swelling, instability of the knee |
| Complications | Vascular injury, nerve injury, compartment syndrome |
| Onset | Sudden, often due to trauma |
| Duration | Varies, depending on severity and treatment |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | High-energy trauma, sports injuries, falls |
| Risks | Obesity, previous knee injuries |
| Diagnosis | Physical examination, X-ray, MRI |
| Differential diagnosis | Knee sprain, knee fracture, patellar dislocation |
| Prevention | Protective gear, strength training |
| Treatment | Reduction (orthopedic), surgery, physical therapy |
| Medication | N/A |
| Prognosis | Varies, potential for chronic pain and arthritis |
| Frequency | Rare |
| Deaths | N/A |



Knee dislocation
A knee dislocation is a severe injury that occurs when the bones that form the knee joint are out of place. This condition is different from a patellar dislocation, which involves the displacement of the kneecap. Knee dislocations are often the result of high-energy trauma, such as car accidents or sports injuries.
Anatomy of the Knee
The knee joint is composed of three bones: the femur (thigh bone), the tibia (shin bone), and the patella (kneecap). These bones are connected by a complex network of ligaments, including the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL), posterior cruciate ligament (PCL), medial collateral ligament (MCL), and lateral collateral ligament (LCL). The knee also contains cartilage and menisci that cushion the joint and facilitate smooth movement.
Causes
Knee dislocations are typically caused by high-impact trauma. Common causes include:
- Motor vehicle accidents
- Sports injuries
- Falls from significant heights
- Industrial accidents
Symptoms
Symptoms of a knee dislocation may include:
- Severe pain
- Visible deformity of the knee
- Swelling and bruising
- Inability to move the knee
- Numbness or tingling if nerves are affected
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of a knee dislocation is usually made through a combination of physical examination and imaging studies. X-rays and MRI scans are commonly used to assess the extent of the injury and to check for associated damage to ligaments, blood vessels, and nerves.
Treatment
Treatment for a knee dislocation often involves:
- Immediate reduction (realignment) of the dislocated knee
- Immobilization with a splint or brace
- Surgery to repair damaged ligaments, blood vessels, or nerves
- Physical therapy to restore function and strength
Complications
Complications from knee dislocations can be severe and may include:
- Vascular injury: Damage to the popliteal artery can lead to compromised blood flow and may require emergency surgery.
- Nerve injury: Damage to the peroneal nerve can result in foot drop and other neurological deficits.
- Chronic instability: Persistent instability of the knee joint may occur if ligaments do not heal properly.
- Arthritis: Post-traumatic arthritis can develop in the affected knee joint over time.
Prognosis
The prognosis for a knee dislocation depends on the severity of the injury and the promptness of treatment. Early and appropriate management can lead to good functional outcomes, although some patients may experience long-term complications.
See also
References
<references group="" responsive="1"></references>
External links
