Hanhart syndrome: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{SI}} | |||
{{Infobox medical condition | |||
| name = Hanhart syndrome | |||
| image = [[File:Infant_with_Möbius_syndrome.jpg|alt=Infant with Möbius syndrome]] | |||
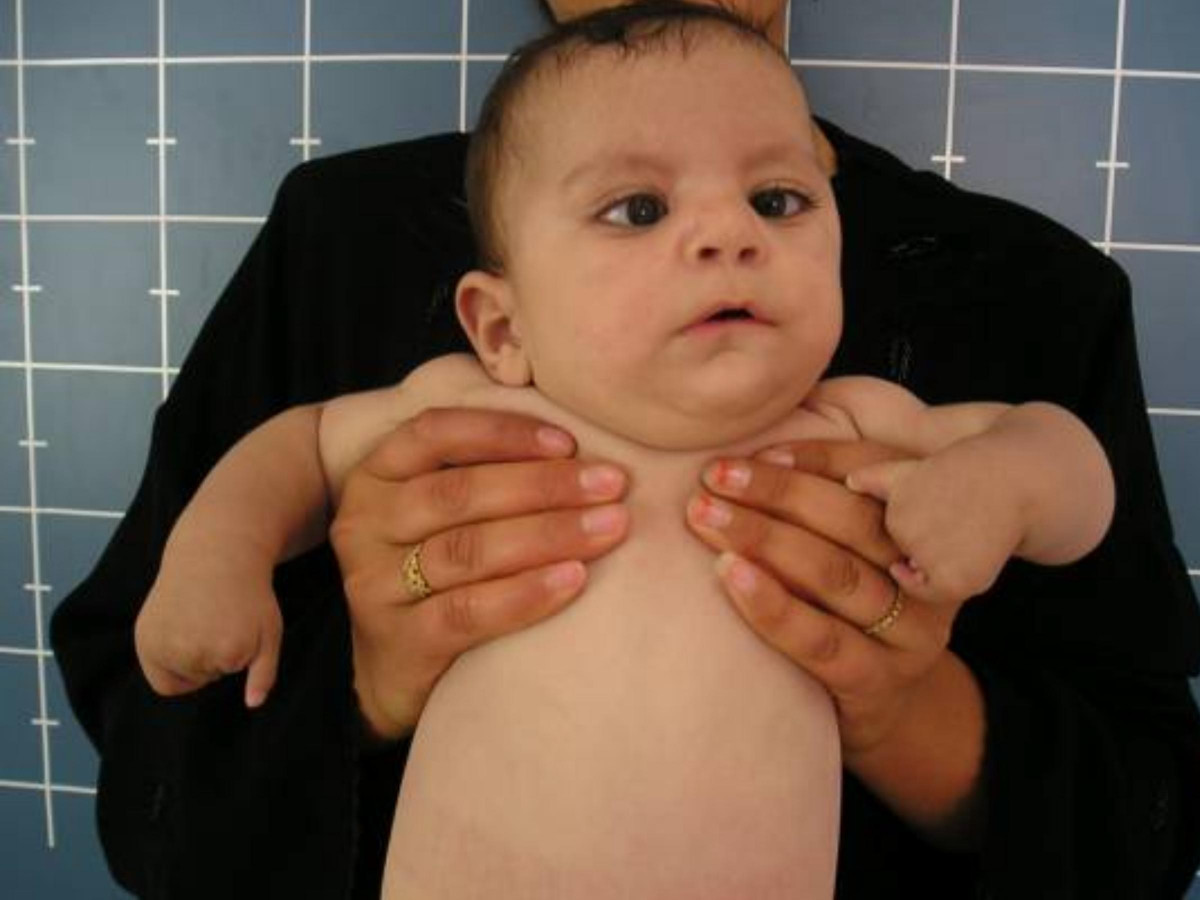
| caption = Infant with Möbius syndrome, a condition sometimes associated with Hanhart syndrome | |||
| field = [[Medical genetics]] | |||
| synonyms = [[Aglossia-adactylia syndrome]], [[Peromelia with micrognathia and microglossia]] | |||
| symptoms = [[Hypoglossia]], [[hypodactylia]], [[micrognathia]], [[cleft palate]] | |||
| complications = [[Feeding difficulties]], [[speech difficulties]] | |||
| onset = [[Congenital]] | |||
| duration = [[Lifelong]] | |||
| causes = [[Genetic mutation]] | |||
| risks = [[Family history]] | |||
| diagnosis = [[Clinical examination]], [[genetic testing]] | |||
| differential = [[Moebius syndrome]], [[oromandibular limb hypogenesis syndrome]] | |||
| treatment = [[Supportive care]], [[surgical intervention]] | |||
| prognosis = [[Variable]] | |||
| frequency = [[Rare]] | |||
}} | |||
{{Short description|A rare congenital disorder affecting limb and craniofacial development}} | {{Short description|A rare congenital disorder affecting limb and craniofacial development}} | ||
'''Hanhart syndrome''' is a rare congenital disorder characterized by limb and craniofacial abnormalities. It is a type of [[oromandibular limb hypogenesis syndrome]], which involves underdevelopment of the mouth, jaw, and limbs. The condition is named after the German physician [[Egon Hanhart]], who first described it in the 1950s. | '''Hanhart syndrome''' is a rare congenital disorder characterized by limb and craniofacial abnormalities. It is a type of [[oromandibular limb hypogenesis syndrome]], which involves underdevelopment of the mouth, jaw, and limbs. The condition is named after the German physician [[Egon Hanhart]], who first described it in the 1950s. | ||
==Presentation== | ==Presentation== | ||
Individuals with Hanhart syndrome typically present with a combination of [[micrognathia]] (small jaw), [[glossoptosis]] (downward displacement or retraction of the tongue), and limb defects. The limb defects can vary significantly in severity and may include [[hypoplasia]] or [[aplasia]] of the fingers, toes, hands, or feet. In some cases, individuals may have [[syndactyly]] (fusion of fingers or toes) or [[polydactyly]] (extra fingers or toes). | Individuals with Hanhart syndrome typically present with a combination of [[micrognathia]] (small jaw), [[glossoptosis]] (downward displacement or retraction of the tongue), and limb defects. The limb defects can vary significantly in severity and may include [[hypoplasia]] or [[aplasia]] of the fingers, toes, hands, or feet. In some cases, individuals may have [[syndactyly]] (fusion of fingers or toes) or [[polydactyly]] (extra fingers or toes). | ||
==Etiology== | ==Etiology== | ||
The exact cause of Hanhart syndrome is not well understood. It is believed to be a genetic disorder, although the specific genetic mutations involved have not been definitively identified. Some cases have been associated with [[chromosomal abnormalities]], but these are not consistent across all individuals with the syndrome. | The exact cause of Hanhart syndrome is not well understood. It is believed to be a genetic disorder, although the specific genetic mutations involved have not been definitively identified. Some cases have been associated with [[chromosomal abnormalities]], but these are not consistent across all individuals with the syndrome. | ||
==Diagnosis== | ==Diagnosis== | ||
Diagnosis of Hanhart syndrome is primarily based on clinical examination and the identification of characteristic physical features. [[Prenatal diagnosis]] may be possible through [[ultrasound]] if limb and craniofacial abnormalities are detected. Genetic testing may be used to rule out other conditions with similar presentations. | Diagnosis of Hanhart syndrome is primarily based on clinical examination and the identification of characteristic physical features. [[Prenatal diagnosis]] may be possible through [[ultrasound]] if limb and craniofacial abnormalities are detected. Genetic testing may be used to rule out other conditions with similar presentations. | ||
==Management== | ==Management== | ||
Management of Hanhart syndrome is typically supportive and symptomatic. Surgical interventions may be necessary to address significant limb deformities or craniofacial abnormalities. [[Speech therapy]] and [[occupational therapy]] can be beneficial in improving functional outcomes and quality of life. Multidisciplinary care involving [[pediatricians]], [[geneticists]], [[orthopedic surgeons]], and other specialists is often required. | Management of Hanhart syndrome is typically supportive and symptomatic. Surgical interventions may be necessary to address significant limb deformities or craniofacial abnormalities. [[Speech therapy]] and [[occupational therapy]] can be beneficial in improving functional outcomes and quality of life. Multidisciplinary care involving [[pediatricians]], [[geneticists]], [[orthopedic surgeons]], and other specialists is often required. | ||
==Prognosis== | ==Prognosis== | ||
The prognosis for individuals with Hanhart syndrome varies depending on the severity of the abnormalities and the presence of any associated complications. Early intervention and comprehensive management can improve outcomes and help individuals achieve a better quality of life. | The prognosis for individuals with Hanhart syndrome varies depending on the severity of the abnormalities and the presence of any associated complications. Early intervention and comprehensive management can improve outcomes and help individuals achieve a better quality of life. | ||
==See also== | |||
== | |||
* [[Oromandibular limb hypogenesis syndrome]] | * [[Oromandibular limb hypogenesis syndrome]] | ||
* [[Micrognathia]] | * [[Micrognathia]] | ||
| Line 24: | Line 36: | ||
* [[Syndactyly]] | * [[Syndactyly]] | ||
* [[Polydactyly]] | * [[Polydactyly]] | ||
[[Category:Congenital disorders]] | [[Category:Congenital disorders]] | ||
[[Category:Rare diseases]] | [[Category:Rare diseases]] | ||
[[Category:Syndromes affecting the jaw]] | [[Category:Syndromes affecting the jaw]] | ||
[[Category:Syndromes with craniofacial abnormalities]] | [[Category:Syndromes with craniofacial abnormalities]] | ||
Latest revision as of 04:26, 7 April 2025

Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD medical weight loss NYC and sleep center NYC
| Hanhart syndrome | |
|---|---|
| |
| Synonyms | Aglossia-adactylia syndrome, Peromelia with micrognathia and microglossia |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Hypoglossia, hypodactylia, micrognathia, cleft palate |
| Complications | Feeding difficulties, speech difficulties |
| Onset | Congenital |
| Duration | Lifelong |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Genetic mutation |
| Risks | Family history |
| Diagnosis | Clinical examination, genetic testing |
| Differential diagnosis | Moebius syndrome, oromandibular limb hypogenesis syndrome |
| Prevention | N/A |
| Treatment | Supportive care, surgical intervention |
| Medication | N/A |
| Prognosis | Variable |
| Frequency | Rare |
| Deaths | N/A |
A rare congenital disorder affecting limb and craniofacial development
Hanhart syndrome is a rare congenital disorder characterized by limb and craniofacial abnormalities. It is a type of oromandibular limb hypogenesis syndrome, which involves underdevelopment of the mouth, jaw, and limbs. The condition is named after the German physician Egon Hanhart, who first described it in the 1950s.
Presentation[edit]
Individuals with Hanhart syndrome typically present with a combination of micrognathia (small jaw), glossoptosis (downward displacement or retraction of the tongue), and limb defects. The limb defects can vary significantly in severity and may include hypoplasia or aplasia of the fingers, toes, hands, or feet. In some cases, individuals may have syndactyly (fusion of fingers or toes) or polydactyly (extra fingers or toes).
Etiology[edit]
The exact cause of Hanhart syndrome is not well understood. It is believed to be a genetic disorder, although the specific genetic mutations involved have not been definitively identified. Some cases have been associated with chromosomal abnormalities, but these are not consistent across all individuals with the syndrome.
Diagnosis[edit]
Diagnosis of Hanhart syndrome is primarily based on clinical examination and the identification of characteristic physical features. Prenatal diagnosis may be possible through ultrasound if limb and craniofacial abnormalities are detected. Genetic testing may be used to rule out other conditions with similar presentations.
Management[edit]
Management of Hanhart syndrome is typically supportive and symptomatic. Surgical interventions may be necessary to address significant limb deformities or craniofacial abnormalities. Speech therapy and occupational therapy can be beneficial in improving functional outcomes and quality of life. Multidisciplinary care involving pediatricians, geneticists, orthopedic surgeons, and other specialists is often required.
Prognosis[edit]
The prognosis for individuals with Hanhart syndrome varies depending on the severity of the abnormalities and the presence of any associated complications. Early intervention and comprehensive management can improve outcomes and help individuals achieve a better quality of life.