Electrical injury: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{SI}} | |||
{{Infobox medical condition | |||
| name = Electrical injury | |||
| image = [[File:Lightning_injury.jpg|250px]] | |||
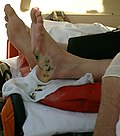
| caption = Skin lesions from a lightning strike | |||
| field = [[Emergency medicine]] | |||
| symptoms = [[Burn]]s, [[cardiac arrest]], [[muscle pain]], [[numbness]] | |||
| complications = [[Cardiac arrhythmia]], [[compartment syndrome]], [[rhabdomyolysis]], [[neurological damage]] | |||
| onset = Immediate | |||
| duration = Varies | |||
| causes = [[Electric shock]], [[lightning strike]] | |||
| risks = [[Occupational hazard]], [[outdoor activities]] | |||
| diagnosis = Based on [[history]] and [[physical examination]] | |||
| differential = [[Thermal burn]], [[chemical burn]], [[trauma]] | |||
| prevention = [[Safety equipment]], [[grounding]], [[lightning protection]] | |||
| treatment = [[Resuscitation]], [[wound care]], [[pain management]], [[cardiac monitoring]] | |||
| prognosis = Depends on severity and promptness of treatment | |||
| frequency = Common in [[industrial settings]] and during [[thunderstorms]] | |||
}} | |||
'''Electrical injury''' refers to damage to the body caused by an external electric current. This type of injury can occur in various contexts, ranging from accidental contact with household electricity to lightning strikes. The severity of an electrical injury can vary widely, from minor skin burns to life-threatening conditions such as cardiac arrest and severe muscle damage. Understanding the mechanisms, types, treatment, and prevention of electrical injuries is crucial for both medical professionals and the general public. | '''Electrical injury''' refers to damage to the body caused by an external electric current. This type of injury can occur in various contexts, ranging from accidental contact with household electricity to lightning strikes. The severity of an electrical injury can vary widely, from minor skin burns to life-threatening conditions such as cardiac arrest and severe muscle damage. Understanding the mechanisms, types, treatment, and prevention of electrical injuries is crucial for both medical professionals and the general public. | ||
==Mechanisms of Injury== | ==Mechanisms of Injury== | ||
Electrical injuries occur when an electric current passes through the body. The damage caused by the current depends on several factors, including the type of current (alternating current (AC) or direct current (DC)), the pathway of the current through the body, the voltage, and the duration of exposure. AC is more dangerous than DC because it causes muscle tetany, which increases the risk of prolonged contact. The resistance of the body also plays a significant role, with lower resistance pathways (such as those involving the heart or nervous system) being more susceptible to injury. | Electrical injuries occur when an electric current passes through the body. The damage caused by the current depends on several factors, including the type of current (alternating current (AC) or direct current (DC)), the pathway of the current through the body, the voltage, and the duration of exposure. AC is more dangerous than DC because it causes muscle tetany, which increases the risk of prolonged contact. The resistance of the body also plays a significant role, with lower resistance pathways (such as those involving the heart or nervous system) being more susceptible to injury. | ||
==Types of Electrical Injury== | ==Types of Electrical Injury== | ||
Electrical injuries can be classified into several types: | Electrical injuries can be classified into several types: | ||
1. '''Surface Burns:''' These occur at the points of contact with the electrical source and are usually visible on the skin. | 1. '''Surface Burns:''' These occur at the points of contact with the electrical source and are usually visible on the skin. | ||
2. '''Internal Injuries:''' These are more dangerous and can affect the heart, muscles, and nervous system. Symptoms may not be immediately apparent. | 2. '''Internal Injuries:''' These are more dangerous and can affect the heart, muscles, and nervous system. Symptoms may not be immediately apparent. | ||
| Line 12: | Line 28: | ||
4. '''Flash Burns:''' These are superficial burns caused by the flash of heat from an electrical explosion and do not involve current passing through the body. | 4. '''Flash Burns:''' These are superficial burns caused by the flash of heat from an electrical explosion and do not involve current passing through the body. | ||
5. '''Blast Injuries:''' The force of an electrical explosion can cause physical trauma, such as blunt force injuries. | 5. '''Blast Injuries:''' The force of an electrical explosion can cause physical trauma, such as blunt force injuries. | ||
==Diagnosis and Treatment== | ==Diagnosis and Treatment== | ||
Diagnosis of electrical injury involves a thorough medical history and physical examination, focusing on the extent and depth of burns, cardiac monitoring, and assessment of muscle damage. Imaging tests, such as X-rays or MRIs, may be necessary to evaluate internal injuries. | Diagnosis of electrical injury involves a thorough medical history and physical examination, focusing on the extent and depth of burns, cardiac monitoring, and assessment of muscle damage. Imaging tests, such as X-rays or MRIs, may be necessary to evaluate internal injuries. | ||
Treatment depends on the severity and type of injury. It may include: | Treatment depends on the severity and type of injury. It may include: | ||
* Burn care, including cleaning and dressing of wounds. | |||
* Pain management. | |||
* Monitoring and treating cardiac irregularities. | |||
* Fluid replacement and electrolyte balance to prevent kidney damage from muscle breakdown products. | |||
* Physical therapy to address muscle and tissue damage. | |||
==Prevention== | ==Prevention== | ||
Preventing electrical injuries involves both public education and safety measures, such as: | Preventing electrical injuries involves both public education and safety measures, such as: | ||
* Use of ground-fault circuit interrupters (GFCIs) in high-risk areas. | |||
* Regular inspection and maintenance of electrical equipment. | |||
* Use of personal protective equipment (PPE) for electrical workers. | |||
* Public education campaigns on the dangers of electricity and safe practices. | |||
==Images== | |||
== | |||
<gallery> | <gallery> | ||
File:Verbrennung_Grad_2b.jpg|Second-degree burn | File:Verbrennung_Grad_2b.jpg|Second-degree burn | ||
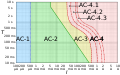
File:IEC_TS_60479-1_electric_shock_graph.svg|Electric shock graph | File:IEC_TS_60479-1_electric_shock_graph.svg|Electric shock graph | ||
| Line 46: | Line 50: | ||
File:Singchair.jpg|Electrical injury | File:Singchair.jpg|Electrical injury | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
==Summary== | |||
Electrical injuries are a significant health risk that can cause a wide range of symptoms and long-term effects. Prompt diagnosis and treatment are essential for minimizing damage and ensuring a good outcome. Prevention efforts and public education are key to reducing the incidence of these potentially devastating injuries. | |||
[[Category:Injuries]] | |||
[[Category:Electrical safety]] | |||
[[Category:Medical emergencies]] | |||
{{medicine-stub}} | |||
Latest revision as of 15:06, 6 April 2025

Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD medical weight loss NYC and sleep center NYC
| Electrical injury | |
|---|---|

| |
| Synonyms | N/A |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Burns, cardiac arrest, muscle pain, numbness |
| Complications | Cardiac arrhythmia, compartment syndrome, rhabdomyolysis, neurological damage |
| Onset | Immediate |
| Duration | Varies |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Electric shock, lightning strike |
| Risks | Occupational hazard, outdoor activities |
| Diagnosis | Based on history and physical examination |
| Differential diagnosis | Thermal burn, chemical burn, trauma |
| Prevention | Safety equipment, grounding, lightning protection |
| Treatment | Resuscitation, wound care, pain management, cardiac monitoring |
| Medication | N/A |
| Prognosis | Depends on severity and promptness of treatment |
| Frequency | Common in industrial settings and during thunderstorms |
| Deaths | N/A |
Electrical injury refers to damage to the body caused by an external electric current. This type of injury can occur in various contexts, ranging from accidental contact with household electricity to lightning strikes. The severity of an electrical injury can vary widely, from minor skin burns to life-threatening conditions such as cardiac arrest and severe muscle damage. Understanding the mechanisms, types, treatment, and prevention of electrical injuries is crucial for both medical professionals and the general public.
Mechanisms of Injury[edit]
Electrical injuries occur when an electric current passes through the body. The damage caused by the current depends on several factors, including the type of current (alternating current (AC) or direct current (DC)), the pathway of the current through the body, the voltage, and the duration of exposure. AC is more dangerous than DC because it causes muscle tetany, which increases the risk of prolonged contact. The resistance of the body also plays a significant role, with lower resistance pathways (such as those involving the heart or nervous system) being more susceptible to injury.
Types of Electrical Injury[edit]
Electrical injuries can be classified into several types: 1. Surface Burns: These occur at the points of contact with the electrical source and are usually visible on the skin. 2. Internal Injuries: These are more dangerous and can affect the heart, muscles, and nervous system. Symptoms may not be immediately apparent. 3. Arc Burns: Caused by high temperatures generated by an electrical arc, these burns can cause severe tissue damage. 4. Flash Burns: These are superficial burns caused by the flash of heat from an electrical explosion and do not involve current passing through the body. 5. Blast Injuries: The force of an electrical explosion can cause physical trauma, such as blunt force injuries.
Diagnosis and Treatment[edit]
Diagnosis of electrical injury involves a thorough medical history and physical examination, focusing on the extent and depth of burns, cardiac monitoring, and assessment of muscle damage. Imaging tests, such as X-rays or MRIs, may be necessary to evaluate internal injuries. Treatment depends on the severity and type of injury. It may include:
- Burn care, including cleaning and dressing of wounds.
- Pain management.
- Monitoring and treating cardiac irregularities.
- Fluid replacement and electrolyte balance to prevent kidney damage from muscle breakdown products.
- Physical therapy to address muscle and tissue damage.
Prevention[edit]
Preventing electrical injuries involves both public education and safety measures, such as:
- Use of ground-fault circuit interrupters (GFCIs) in high-risk areas.
- Regular inspection and maintenance of electrical equipment.
- Use of personal protective equipment (PPE) for electrical workers.
- Public education campaigns on the dangers of electricity and safe practices.
Images[edit]
-
Second-degree burn
-
Electric shock graph
-
Electrical injury
-
Electrical injury
-
Electrical injury
Summary[edit]
Electrical injuries are a significant health risk that can cause a wide range of symptoms and long-term effects. Prompt diagnosis and treatment are essential for minimizing damage and ensuring a good outcome. Prevention efforts and public education are key to reducing the incidence of these potentially devastating injuries.