Myelitis: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{SI}} | |||
{{Infobox medical condition | |||
| name = Myelitis | |||
| image = [[File:Nerve.nida.jpg|250px]] | |||
| caption = Illustration of nerve inflammation | |||
| field = [[Neurology]] | |||
| symptoms = [[Back pain]], [[muscle weakness]], [[paralysis]], [[sensory loss]] | |||
| complications = [[Chronic pain]], [[disability]], [[bladder dysfunction]] | |||
| onset = Sudden or gradual | |||
| duration = Varies | |||
| causes = [[Infection]], [[autoimmune disease]], [[multiple sclerosis]], [[vascular disorders]] | |||
| risks = [[Viral infections]], [[bacterial infections]], [[autoimmune disorders]] | |||
| diagnosis = [[MRI]], [[lumbar puncture]], [[blood tests]] | |||
| differential = [[Multiple sclerosis]], [[spinal cord injury]], [[Guillain-Barré syndrome]] | |||
| treatment = [[Corticosteroids]], [[plasmapheresis]], [[immunosuppressive drugs]] | |||
| prognosis = Varies; some recover fully, others may have permanent deficits | |||
| frequency = Rare | |||
}} | |||
'''Myelitis''' is an [[inflammation]] of the [[spinal cord]], which can disrupt the normal responses from the brain to the rest of the body, and from the rest of the body to the brain. Myelitis can occur in children and adults, in both males and females. It is a rare condition, affecting approximately one in a million people. | '''Myelitis''' is an [[inflammation]] of the [[spinal cord]], which can disrupt the normal responses from the brain to the rest of the body, and from the rest of the body to the brain. Myelitis can occur in children and adults, in both males and females. It is a rare condition, affecting approximately one in a million people. | ||
== Causes == | == Causes == | ||
Myelitis is often caused by [[infections]] that inflame the spinal cord. These infections can be caused by [[viruses]], [[bacteria]], or [[parasites]]. Other causes of myelitis include [[autoimmune diseases]] such as [[multiple sclerosis]], [[neuromyelitis optica]], and [[acute disseminated encephalomyelitis]]. | Myelitis is often caused by [[infections]] that inflame the spinal cord. These infections can be caused by [[viruses]], [[bacteria]], or [[parasites]]. Other causes of myelitis include [[autoimmune diseases]] such as [[multiple sclerosis]], [[neuromyelitis optica]], and [[acute disseminated encephalomyelitis]]. | ||
== Symptoms == | == Symptoms == | ||
Symptoms of myelitis can vary widely, depending on the area of the spinal cord that is affected. Common symptoms include [[pain]], [[weakness]], [[numbness]], and [[bladder dysfunction]]. In severe cases, myelitis can cause [[paralysis]]. | Symptoms of myelitis can vary widely, depending on the area of the spinal cord that is affected. Common symptoms include [[pain]], [[weakness]], [[numbness]], and [[bladder dysfunction]]. In severe cases, myelitis can cause [[paralysis]]. | ||
== Diagnosis == | == Diagnosis == | ||
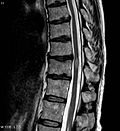
Diagnosis of myelitis is typically made through a combination of [[medical history]], [[physical examination]], and [[imaging studies]]. [[Magnetic resonance imaging]] (MRI) is often used to visualize the spinal cord and identify areas of inflammation. | Diagnosis of myelitis is typically made through a combination of [[medical history]], [[physical examination]], and [[imaging studies]]. [[Magnetic resonance imaging]] (MRI) is often used to visualize the spinal cord and identify areas of inflammation. | ||
== Treatment == | == Treatment == | ||
Treatment for myelitis is aimed at reducing inflammation in the spinal cord and managing symptoms. This may include [[corticosteroids]], [[plasma exchange therapy]], and [[physical therapy]]. In some cases, treatment for the underlying cause of the myelitis, such as an infection or autoimmune disease, may also be necessary. | Treatment for myelitis is aimed at reducing inflammation in the spinal cord and managing symptoms. This may include [[corticosteroids]], [[plasma exchange therapy]], and [[physical therapy]]. In some cases, treatment for the underlying cause of the myelitis, such as an infection or autoimmune disease, may also be necessary. | ||
== Prognosis == | == Prognosis == | ||
The prognosis for individuals with myelitis varies. Some individuals may recover with minor or no residual problems, while others may have significant long-term disabilities. | The prognosis for individuals with myelitis varies. Some individuals may recover with minor or no residual problems, while others may have significant long-term disabilities. | ||
==Gallery== | |||
<gallery> | |||
File:Transverse myelitis MRI.jpg|Myelitis | |||
File:Polio spinal diagram-en.svg|Myelitis | |||
</gallery> | |||
== See also == | == See also == | ||
* [[Transverse myelitis]] | * [[Transverse myelitis]] | ||
| Line 21: | Line 38: | ||
* [[Multiple sclerosis]] | * [[Multiple sclerosis]] | ||
* [[Neuromyelitis optica]] | * [[Neuromyelitis optica]] | ||
[[Category:Neurological disorders]] | [[Category:Neurological disorders]] | ||
[[Category:Inflammations]] | [[Category:Inflammations]] | ||
[[Category:Spinal cord disorders]] | [[Category:Spinal cord disorders]] | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
Latest revision as of 04:43, 6 April 2025

Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD's medical weight loss NYC, sleep center NYC
Philadelphia medical weight loss and Philadelphia sleep clinics
| Myelitis | |
|---|---|

| |
| Synonyms | N/A |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Back pain, muscle weakness, paralysis, sensory loss |
| Complications | Chronic pain, disability, bladder dysfunction |
| Onset | Sudden or gradual |
| Duration | Varies |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Infection, autoimmune disease, multiple sclerosis, vascular disorders |
| Risks | Viral infections, bacterial infections, autoimmune disorders |
| Diagnosis | MRI, lumbar puncture, blood tests |
| Differential diagnosis | Multiple sclerosis, spinal cord injury, Guillain-Barré syndrome |
| Prevention | N/A |
| Treatment | Corticosteroids, plasmapheresis, immunosuppressive drugs |
| Medication | N/A |
| Prognosis | Varies; some recover fully, others may have permanent deficits |
| Frequency | Rare |
| Deaths | N/A |
Myelitis is an inflammation of the spinal cord, which can disrupt the normal responses from the brain to the rest of the body, and from the rest of the body to the brain. Myelitis can occur in children and adults, in both males and females. It is a rare condition, affecting approximately one in a million people.
Causes[edit]
Myelitis is often caused by infections that inflame the spinal cord. These infections can be caused by viruses, bacteria, or parasites. Other causes of myelitis include autoimmune diseases such as multiple sclerosis, neuromyelitis optica, and acute disseminated encephalomyelitis.
Symptoms[edit]
Symptoms of myelitis can vary widely, depending on the area of the spinal cord that is affected. Common symptoms include pain, weakness, numbness, and bladder dysfunction. In severe cases, myelitis can cause paralysis.
Diagnosis[edit]
Diagnosis of myelitis is typically made through a combination of medical history, physical examination, and imaging studies. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is often used to visualize the spinal cord and identify areas of inflammation.
Treatment[edit]
Treatment for myelitis is aimed at reducing inflammation in the spinal cord and managing symptoms. This may include corticosteroids, plasma exchange therapy, and physical therapy. In some cases, treatment for the underlying cause of the myelitis, such as an infection or autoimmune disease, may also be necessary.
Prognosis[edit]
The prognosis for individuals with myelitis varies. Some individuals may recover with minor or no residual problems, while others may have significant long-term disabilities.
Gallery[edit]
-
Myelitis
-
Myelitis