Hypercementosis: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{SI}} | |||
{{Infobox medical condition | |||
| name = Hypercementosis | |||
| image = [[File:Labeledmolar.jpg|250px]] | |||
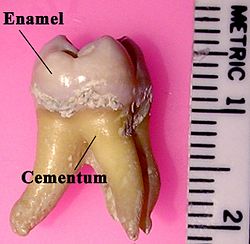
| caption = Labeled diagram of a molar tooth | |||
| field = [[Dentistry]] | |||
| synonyms = Cementum hyperplasia | |||
| symptoms = Often asymptomatic, may cause [[tooth pain]] if associated with other conditions | |||
| complications = May complicate [[tooth extraction]] | |||
| onset = Usually detected in adults | |||
| duration = Chronic | |||
| causes = Unknown, but associated with [[Paget's disease of bone]], [[acromegaly]], and [[hyperpituitarism]] | |||
| risks = [[Bruxism]], [[trauma]], [[inflammation]] | |||
| diagnosis = [[Dental radiography]] | |||
| differential = [[Cementoblastoma]], [[periapical cemental dysplasia]] | |||
| prevention = None specific | |||
| treatment = Generally not required unless symptomatic | |||
| prognosis = Good, as it is usually benign | |||
| frequency = Relatively uncommon | |||
}} | |||
{{Short description|An overview of hypercementosis, a dental condition}} | {{Short description|An overview of hypercementosis, a dental condition}} | ||
'''Hypercementosis''' is a dental condition characterized by the excessive formation of [[cementum]] on the roots of one or more teeth. Cementum is a calcified tissue that covers the roots of teeth and helps anchor them to the [[alveolar bone]] via the [[periodontal ligament]]. | '''Hypercementosis''' is a dental condition characterized by the excessive formation of [[cementum]] on the roots of one or more teeth. Cementum is a calcified tissue that covers the roots of teeth and helps anchor them to the [[alveolar bone]] via the [[periodontal ligament]]. | ||
== Etiology == | == Etiology == | ||
The exact cause of hypercementosis is not well understood, but it is believed to be associated with several factors, including: | The exact cause of hypercementosis is not well understood, but it is believed to be associated with several factors, including: | ||
| Line 10: | Line 29: | ||
* [[Thyroid]] disorders | * [[Thyroid]] disorders | ||
* [[Idiopathic]] causes | * [[Idiopathic]] causes | ||
== Clinical Features == | == Clinical Features == | ||
Hypercementosis is often asymptomatic and is usually discovered incidentally on [[dental radiographs]]. In some cases, it may cause difficulty during [[tooth extraction]] due to the increased bulk of the root. | Hypercementosis is often asymptomatic and is usually discovered incidentally on [[dental radiographs]]. In some cases, it may cause difficulty during [[tooth extraction]] due to the increased bulk of the root. | ||
== Diagnosis == | == Diagnosis == | ||
The diagnosis of hypercementosis is primarily made through radiographic examination. On an [[X-ray]], affected teeth show an increased radiopacity at the root apex, indicating the presence of excess cementum. | The diagnosis of hypercementosis is primarily made through radiographic examination. On an [[X-ray]], affected teeth show an increased radiopacity at the root apex, indicating the presence of excess cementum. | ||
== Treatment == | == Treatment == | ||
In most cases, hypercementosis does not require treatment unless it is associated with other dental issues or complicates dental procedures. If extraction is necessary, surgical intervention may be required to manage the enlarged root structure. | In most cases, hypercementosis does not require treatment unless it is associated with other dental issues or complicates dental procedures. If extraction is necessary, surgical intervention may be required to manage the enlarged root structure. | ||
== See Also == | |||
== | |||
* [[Cementum]] | * [[Cementum]] | ||
* [[Periodontal ligament]] | * [[Periodontal ligament]] | ||
* [[Tooth anatomy]] | * [[Tooth anatomy]] | ||
* [[Dental radiography]] | * [[Dental radiography]] | ||
[[Category:Dental conditions]] | [[Category:Dental conditions]] | ||
Latest revision as of 02:36, 6 April 2025

Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD's medical weight loss NYC, sleep center NYC
Philadelphia medical weight loss and Philadelphia sleep clinics
| Hypercementosis | |
|---|---|
| |
| Synonyms | Cementum hyperplasia |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Often asymptomatic, may cause tooth pain if associated with other conditions |
| Complications | May complicate tooth extraction |
| Onset | Usually detected in adults |
| Duration | Chronic |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Unknown, but associated with Paget's disease of bone, acromegaly, and hyperpituitarism |
| Risks | Bruxism, trauma, inflammation |
| Diagnosis | Dental radiography |
| Differential diagnosis | Cementoblastoma, periapical cemental dysplasia |
| Prevention | None specific |
| Treatment | Generally not required unless symptomatic |
| Medication | N/A |
| Prognosis | Good, as it is usually benign |
| Frequency | Relatively uncommon |
| Deaths | N/A |
An overview of hypercementosis, a dental condition
Hypercementosis is a dental condition characterized by the excessive formation of cementum on the roots of one or more teeth. Cementum is a calcified tissue that covers the roots of teeth and helps anchor them to the alveolar bone via the periodontal ligament.
Etiology[edit]
The exact cause of hypercementosis is not well understood, but it is believed to be associated with several factors, including:
- Inflammation or trauma to the tooth
- Paget's disease of bone
- Acromegaly
- Arthritis
- Thyroid disorders
- Idiopathic causes
Clinical Features[edit]
Hypercementosis is often asymptomatic and is usually discovered incidentally on dental radiographs. In some cases, it may cause difficulty during tooth extraction due to the increased bulk of the root.
Diagnosis[edit]
The diagnosis of hypercementosis is primarily made through radiographic examination. On an X-ray, affected teeth show an increased radiopacity at the root apex, indicating the presence of excess cementum.
Treatment[edit]
In most cases, hypercementosis does not require treatment unless it is associated with other dental issues or complicates dental procedures. If extraction is necessary, surgical intervention may be required to manage the enlarged root structure.