Frequent urination: Difference between revisions
mNo edit summary |
CSV import |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
= Frequent | {{SI}} | ||
{{Infobox medical condition | |||
== | | name = Frequent urination | ||
| image = [[File:Illu_urinary_system_el.png|250px]] | |||
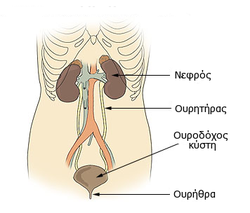
| caption = Diagram of the [[urinary system]] | |||
| field = [[Urology]] | |||
| synonyms = Polyuria | |||
| symptoms = Increased frequency of urination | |||
| complications = [[Dehydration]], [[sleep disturbance]] | |||
| onset = Any age | |||
| duration = Varies | |||
| causes = [[Diabetes mellitus]], [[urinary tract infection]], [[pregnancy]], [[diuretics]] | |||
| risks = [[Diabetes]], [[prostate enlargement]], [[bladder infection]] | |||
| diagnosis = [[Urinalysis]], [[blood test]], [[ultrasound]] | |||
| differential = [[Overactive bladder]], [[interstitial cystitis]], [[prostatitis]] | |||
| prevention = Depends on underlying cause | |||
| treatment = Depends on underlying cause; may include [[medication]], [[lifestyle changes]] | |||
| medication = [[Anticholinergics]], [[antibiotics]] | |||
| frequency = Common | |||
| deaths = Rarely directly | |||
}} | |||
'''Frequent urination''' is a condition characterized by the need to urinate more often than usual. It can affect individuals of all ages and can be a symptom of various underlying health issues. | '''Frequent urination''' is a condition characterized by the need to urinate more often than usual. It can affect individuals of all ages and can be a symptom of various underlying health issues. | ||
== Causes == | == Causes == | ||
Several factors can contribute to frequent urination, including: | Several factors can contribute to frequent urination, including: | ||
* Consumption of diuretics, which increase urine production | * Consumption of diuretics, which increase urine production | ||
| Line 15: | Line 30: | ||
* Overactive bladder syndrome | * Overactive bladder syndrome | ||
* Neurological disorders | * Neurological disorders | ||
<youtube> | <youtube> | ||
title='''{{PAGENAME}}''' | title='''{{PAGENAME}}''' | ||
| Line 26: | Line 40: | ||
height=600 | height=600 | ||
</youtube> | </youtube> | ||
== Nocturia == | == Nocturia == | ||
'''Nocturia''' refers specifically to frequent urination at night, which can disrupt sleep patterns and affect quality of life. | '''Nocturia''' refers specifically to frequent urination at night, which can disrupt sleep patterns and affect quality of life. | ||
== Diagnosis == | == Diagnosis == | ||
Diagnosis of the underlying cause of frequent urination may involve: | Diagnosis of the underlying cause of frequent urination may involve: | ||
| Line 37: | Line 49: | ||
* Cystoscopy | * Cystoscopy | ||
* Urodynamic tests | * Urodynamic tests | ||
== Treatment == | == Treatment == | ||
Treatment for frequent urination depends on the underlying cause: | Treatment for frequent urination depends on the underlying cause: | ||
| Line 44: | Line 55: | ||
* Lifestyle modifications, like reducing fluid intake before bedtime for nocturia | * Lifestyle modifications, like reducing fluid intake before bedtime for nocturia | ||
* Bladder training exercises | * Bladder training exercises | ||
== Prevention == | == Prevention == | ||
Preventive measures can include: | Preventive measures can include: | ||
| Line 50: | Line 60: | ||
* Regularly emptying the bladder | * Regularly emptying the bladder | ||
* Avoiding excessive consumption of diuretics | * Avoiding excessive consumption of diuretics | ||
== Epidemiology == | == Epidemiology == | ||
The prevalence of frequent urination varies, with certain groups like older adults and pregnant women being more commonly affected. | The prevalence of frequent urination varies, with certain groups like older adults and pregnant women being more commonly affected. | ||
== See Also == | == See Also == | ||
* [[Prostate Health]] | * [[Prostate Health]] | ||
* [[Bladder Control]] | * [[Bladder Control]] | ||
* [[Women's Health]] | * [[Women's Health]] | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
<references> | <references> | ||
| Line 64: | Line 71: | ||
* Patel, S., & Green, M. T. (2022). ''Nocturia: Understanding and Treating Nighttime Urination''. Sleep Medicine Reviews. 27(4), 56-64. | * Patel, S., & Green, M. T. (2022). ''Nocturia: Understanding and Treating Nighttime Urination''. Sleep Medicine Reviews. 27(4), 56-64. | ||
</references> | </references> | ||
== External Links == | == External Links == | ||
* [https://www.urologyhealth.org/urologic-conditions/frequent-urination Urology Care Foundation - Frequent Urination] | * [https://www.urologyhealth.org/urologic-conditions/frequent-urination Urology Care Foundation - Frequent Urination] | ||
| Line 70: | Line 76: | ||
[[Category:Health Conditions]] | [[Category:Health Conditions]] | ||
[[Category:Urology]] | [[Category:Urology]] | ||
[[Category:Dictionary of medicine]]. | [[Category:Dictionary of medicine]]. | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
Latest revision as of 01:58, 6 April 2025

Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD's medical weight loss NYC, sleep center NYC
Philadelphia medical weight loss and Philadelphia sleep clinics
| Frequent urination | |
|---|---|
| |
| Synonyms | Polyuria |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Increased frequency of urination |
| Complications | Dehydration, sleep disturbance |
| Onset | Any age |
| Duration | Varies |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Diabetes mellitus, urinary tract infection, pregnancy, diuretics |
| Risks | Diabetes, prostate enlargement, bladder infection |
| Diagnosis | Urinalysis, blood test, ultrasound |
| Differential diagnosis | Overactive bladder, interstitial cystitis, prostatitis |
| Prevention | Depends on underlying cause |
| Treatment | Depends on underlying cause; may include medication, lifestyle changes |
| Medication | Anticholinergics, antibiotics |
| Prognosis | N/A |
| Frequency | Common |
| Deaths | Rarely directly |
Frequent urination is a condition characterized by the need to urinate more often than usual. It can affect individuals of all ages and can be a symptom of various underlying health issues.
Causes[edit]
Several factors can contribute to frequent urination, including:
- Consumption of diuretics, which increase urine production
- Urinary tract infection (UTI), particularly common in women and children
- Enlarged prostate in older men
- Diabetes
- Pregnancy
- Overactive bladder syndrome
- Neurological disorders
Nocturia[edit]
Nocturia refers specifically to frequent urination at night, which can disrupt sleep patterns and affect quality of life.
Diagnosis[edit]
Diagnosis of the underlying cause of frequent urination may involve:
- Medical history and physical examination
- Urinalysis
- Ultrasound of the bladder
- Cystoscopy
- Urodynamic tests
Treatment[edit]
Treatment for frequent urination depends on the underlying cause:
- Antibiotics for UTIs
- Medication or surgery for enlarged prostate
- Lifestyle modifications, like reducing fluid intake before bedtime for nocturia
- Bladder training exercises
Prevention[edit]
Preventive measures can include:
- Maintaining good urinary hygiene
- Regularly emptying the bladder
- Avoiding excessive consumption of diuretics
Epidemiology[edit]
The prevalence of frequent urination varies, with certain groups like older adults and pregnant women being more commonly affected.
See Also[edit]
References[edit]
<references>
- Johnson, L. K., & Smith, R. J. (2023). Frequent Urination: Causes and Management. Journal of Urology. 189(2), 123-130.
- Patel, S., & Green, M. T. (2022). Nocturia: Understanding and Treating Nighttime Urination. Sleep Medicine Reviews. 27(4), 56-64.
</references>


