Estradiol phenylpropionate: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 20: | Line 20: | ||
{{Pharmacology-stub}} | {{Pharmacology-stub}} | ||
{{Medicine-stub}} | {{Medicine-stub}} | ||
<gallery> | <gallery> | ||
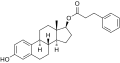
File:Estradiol phenylpropionate structure.svg|Estradiol phenylpropionate structure | File:Estradiol phenylpropionate structure.svg|Estradiol phenylpropionate structure | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
Latest revision as of 20:46, 16 March 2025
Estradiol phenylpropionate (EPP), also known as estradiol phenpropionate, is a synthetic estrogen that is used in hormone replacement therapy (HRT) for the treatment of menopausal symptoms. It is a long-acting estrogen ester and is administered by intramuscular injection.
Pharmacology[edit]
Estradiol phenylpropionate is a prodrug of estradiol, the primary female sex hormone. It works by binding to and activating the estrogen receptor, which in turn influences the expression of many genes in cells throughout the body. This results in a wide range of effects, including the alleviation of menopausal symptoms such as hot flashes and vaginal dryness.
Clinical use[edit]
Estradiol phenylpropionate is used primarily in HRT for menopausal women. It can also be used in the treatment of osteoporosis, certain types of breast cancer, and for feminizing hormone therapy in transgender women.
Side effects[edit]
Like all estrogens, estradiol phenylpropionate can have a number of side effects. These can include nausea, bloating, breast tenderness, and an increased risk of certain types of cancer, such as endometrial cancer. It can also increase the risk of blood clots, stroke, and heart disease in some women.
See also[edit]
-
Estradiol phenylpropionate structure