Substituted cathinone: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 35: | Line 35: | ||
{{Psychoactive substance-stub}} | {{Psychoactive substance-stub}} | ||
{{medicine-stub}} | {{medicine-stub}} | ||
== Substituted cathinone gallery == | |||
<gallery> | |||
File:Cathinone.svg|Cathinone | |||
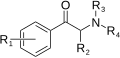
File:Substituted cathinone.svg|Substituted cathinone | |||
File:Cathinone.svg|Cathinone | |||
File:Methcathinone skeletal.svg|Methcathinone | |||
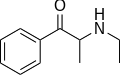
File:Ethcathinone.svg|Ethcathinone | |||
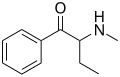
File:Propylcathinone structure.png|Propylcathinone | |||
File:Buphedrone.svg|Buphedrone | |||
File:N-Ethylbuphedrone.svg|N-Ethylbuphedrone | |||
File:Methylethylbuphedrone structure.png|Methylethylbuphedrone | |||
File:Pentedrone.svg|Pentedrone | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 05:52, 3 March 2025
Substituted cathinone is a type of psychoactive compound or designer drug that is chemically similar to cathinone, a naturally occurring stimulant found in the khat plant. Substituted cathinones are part of a larger group of substances known as synthetic cathinones or "bath salts".
History[edit]
The history of substituted cathinones dates back to the 1920s when the first synthetic cathinone, methcathinone, was synthesized. However, it was not until the early 21st century that these substances began to emerge as drugs of abuse, particularly in Europe.
Chemistry[edit]
Substituted cathinones are derived from cathinone by replacing one or more of the hydrogen atoms in the cathinone molecule with other functional groups. The resulting compounds have varying effects on the central nervous system, depending on the nature and position of the substituent.
Effects[edit]
The effects of substituted cathinones can vary widely depending on the specific compound, but they generally include stimulant effects such as increased alertness, euphoria, and increased heart rate. Some substituted cathinones can also have hallucinogenic effects.
Legal status[edit]
The legal status of substituted cathinones varies by country. In many countries, including the United States and the United Kingdom, many substituted cathinones are classified as controlled substances due to their potential for abuse and addiction.
Health risks[edit]
The use of substituted cathinones can pose significant health risks, including cardiovascular problems, neurological damage, and even death. The risk is particularly high when these substances are used in combination with other drugs or alcohol.
See also[edit]
This article is a Psychoactive substance-related stub. You can help WikiMD by expanding it!
Substituted cathinone gallery[edit]
-
Cathinone
-
Substituted cathinone
-
Cathinone
-
Methcathinone
-
Ethcathinone
-
Propylcathinone
-
Buphedrone
-
N-Ethylbuphedrone
-
Methylethylbuphedrone
-
Pentedrone