Chinese Communist Revolution: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 35: | Line 35: | ||
[[Category:20th-century revolutions]] | [[Category:20th-century revolutions]] | ||
[[Category:History of the People's Republic of China]] | [[Category:History of the People's Republic of China]] | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:1967-10 红军时期夹金山.jpg|1967-10 红军时期夹金山 | |||
File:The first flag of China.jpg|The first flag of China | |||
File:中山大学学生抗议美军暴行 02.jpg|中山大学学生抗议美军暴行 02 | |||
File:新青年封面.jpg|新青年封面 | |||
File:Student Demonstrations, June 4th and 5th, 1919 1.jpg|Student Demonstrations, June 4th and 5th, 1919 | |||
File:78 Xingye Lu (3919339998).jpg|78 Xingye Lu | |||
File:Shanghai rev 1927.jpg|Shanghai rev 1927 | |||
File:Wuhan government leaders.png|Wuhan government leaders | |||
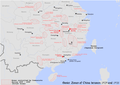
File:China Soviet Zones.png|China Soviet Zones | |||
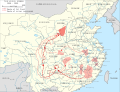
File:Map of the Long March 1934-1935-en.svg|Map of the Long March 1934-1935 | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 05:06, 3 March 2025
An overview of the Chinese Communist Revolution
| History of China |
|---|
|
|
The Chinese Communist Revolution was a pivotal event in the 20th century that led to the establishment of the People's Republic of China (PRC) in 1949. This revolution was the culmination of the Chinese Civil War (1927–1949), which was fought between the Chinese Communist Party (CCP) and the Kuomintang (KMT), the Nationalist Party of China.
Background[edit]
The roots of the Chinese Communist Revolution can be traced back to the early 20th century, during a period of great social and political upheaval in China. The Qing dynasty had fallen in 1911, leading to the establishment of the Republic of China under the leadership of the KMT. However, the new republic was plagued by internal strife, warlordism, and foreign intervention.
The May Fourth Movement of 1919 was a significant cultural and political movement that galvanized Chinese intellectuals and students, leading to increased interest in Marxism and the formation of the CCP in 1921. The CCP initially collaborated with the KMT in the First United Front to end warlord rule and unify China.
The Chinese Civil War[edit]
The alliance between the CCP and KMT broke down in 1927, leading to the outbreak of the Chinese Civil War. The KMT, led by Chiang Kai-shek, sought to eliminate communist influence in China, resulting in the Shanghai Massacre and a series of purges against communists.
The CCP, under the leadership of Mao Zedong, retreated to rural areas and focused on building a base of support among the peasantry. This strategy was exemplified by the Long March (1934–1935), a strategic retreat that solidified Mao's leadership and the CCP's resolve.
World War II and the Second United Front[edit]
The outbreak of the Second Sino-Japanese War in 1937 led to a temporary cessation of hostilities between the CCP and KMT, forming the Second United Front against the Japanese invaders. However, tensions between the two parties persisted, and the civil war resumed after Japan's defeat in 1945.
Victory of the CCP[edit]
The CCP's victory in the civil war was due to several factors, including widespread peasant support, effective guerrilla warfare tactics, and the weakening of the KMT due to corruption and poor governance. By 1949, the CCP had gained control of most of mainland China, and on October 1, 1949, Mao Zedong proclaimed the establishment of the People's Republic of China.
Aftermath[edit]
The establishment of the PRC marked the beginning of a new era in Chinese history. The KMT retreated to Taiwan, where it continued to claim legitimacy as the government of all China. The CCP implemented sweeping land reforms and began the process of transforming China into a socialist state.
Also see[edit]
- Mao Zedong
- Chinese Civil War
- People's Republic of China
- Kuomintang
- Long March
- Second Sino-Japanese War
-
1967-10 红军时期夹金山
-
The first flag of China
-
中山大学学生抗议美军暴行 02
-
新青年封面
-
Student Demonstrations, June 4th and 5th, 1919
-
78 Xingye Lu
-
Shanghai rev 1927
-
Wuhan government leaders
-
China Soviet Zones
-
Map of the Long March 1934-1935