Pradofloxacin: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 39: | Line 39: | ||
[[Category:Antibiotics]] | [[Category:Antibiotics]] | ||
[[Category:Veterinary drugs]] | [[Category:Veterinary drugs]] | ||
<gallery> | |||
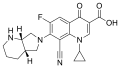
File:Pradofloxacin.svg|Pradofloxacin | |||
</gallery> | |||
<gallery> | <gallery> | ||
File:Pradofloxacin.svg|Pradofloxacin | File:Pradofloxacin.svg|Pradofloxacin | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
Revision as of 01:26, 20 February 2025
An antibiotic used in veterinary medicine
| Pradofloxacin | |
|---|---|

| |
| INN | |
| Drug class | |
| Routes of administration | |
| Pregnancy category | |
| Bioavailability | |
| Metabolism | |
| Elimination half-life | |
| Excretion | |
| Legal status | |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| KEGG | |
Pradofloxacin is a fluoroquinolone antibiotic primarily used in veterinary medicine. It is effective against a broad spectrum of bacteria, including both Gram-positive and Gram-negative organisms. Pradofloxacin is particularly noted for its efficacy in treating infections in cats and dogs.
Mechanism of Action
Pradofloxacin works by inhibiting bacterial DNA gyrase and topoisomerase IV, enzymes critical for DNA replication and transcription. This inhibition leads to the disruption of bacterial DNA synthesis, ultimately resulting in bacterial cell death.
Pharmacokinetics
Pradofloxacin is well absorbed following oral administration. It is distributed widely throughout the body, reaching therapeutic concentrations in various tissues. The drug is metabolized in the liver and excreted primarily via the kidneys.
Clinical Uses
Pradofloxacin is used to treat a variety of infections in animals, including:
It is particularly useful in cases where other antibiotics have failed or when the causative bacteria are resistant to other treatments.
Side Effects
Common side effects of pradofloxacin include gastrointestinal disturbances such as vomiting and diarrhea. In rare cases, it may cause central nervous system effects such as seizures.
Contraindications
Pradofloxacin should not be used in animals with known hypersensitivity to quinolones. It is also contraindicated in young animals due to the risk of cartilage damage.
Related pages
-
Pradofloxacin
-
Pradofloxacin