Uncus: Difference between revisions
From WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia
No edit summary |
CSV import |
||
| Line 40: | Line 40: | ||
{{Neuroanatomy-stub}} | {{Neuroanatomy-stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:Gray727 uncus of parahippocampal gyrus.png|Uncus of parahippocampal gyrus | |||
File:Human brain inferior-medial view description 3.JPG|Inferior-medial view of human brain | |||
File:Uncus animation small.gif|Uncus animation | |||
File:Gehirn, basal - beschriftet lat.svg|Basal view of brain | |||
File:Gray732.png|Uncus | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 01:18, 20 February 2025



== Uncus ==
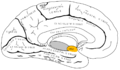
The uncus is a structure located in the medial temporal lobe of the brain. It is part of the parahippocampal gyrus and plays a significant role in the olfactory system and memory processing. The term "uncus" is derived from the Latin word for "hook," reflecting its hook-like shape.
Anatomy[edit]
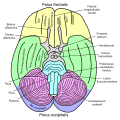
The uncus is situated at the anterior end of the parahippocampal gyrus, adjacent to the hippocampus and the amygdala. It is divided into two parts: the anterior and posterior segments. The anterior segment is involved in the olfactory system, while the posterior segment is associated with the hippocampal formation.
Function[edit]
The primary functions of the uncus include:
- Olfaction: The uncus is closely linked to the olfactory cortex, which is responsible for the sense of smell. It receives input from the olfactory bulb and processes olfactory information.
- Memory: The uncus is part of the limbic system, which is crucial for memory formation and emotional responses. It works in conjunction with the hippocampus to encode and retrieve memories.
Clinical Significance[edit]
The uncus can be involved in various neurological conditions, including:
- Uncal herniation: This occurs when increased intracranial pressure causes the uncus to herniate through the tentorial notch, leading to compression of the brainstem and potentially life-threatening consequences.
- Seizures: Lesions or abnormalities in the uncus can lead to temporal lobe epilepsy, characterized by complex partial seizures.
Related Pages[edit]
- Medial temporal lobe
- Parahippocampal gyrus
- Hippocampus
- Amygdala
- Olfactory system
- Limbic system
- Temporal lobe epilepsy
- Uncal herniation

This article is a neuroanatomy stub. You can help WikiMD by expanding it!
-
Uncus of parahippocampal gyrus
-
Inferior-medial view of human brain
-
Uncus animation
-
Basal view of brain
-
Uncus