N-Ethyl-2C-B: Difference between revisions
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
CSV import |
||
| Line 37: | Line 37: | ||
{{Psychedelic-stub}} | {{Psychedelic-stub}} | ||
{{Pharmacology-stub}} | {{Pharmacology-stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
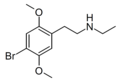
File:Nethyl2CB structure.png|N-Ethyl-2C-B structure | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 01:17, 20 February 2025
N-Ethyl-2C-B or 2C-B-ETH is a psychedelic drug of the 2C family. It was first synthesized by Alexander Shulgin and is considered as an analog of 2C-B.
History[edit]
N-Ethyl-2C-B was first synthesized by Alexander Shulgin, a renowned chemist and psychopharmacologist. Shulgin's extensive work on the 2C family of drugs has contributed significantly to the understanding of these substances.
Chemistry[edit]
N-Ethyl-2C-B is a substituted phenethylamine featuring a phenyl ring bound to an amino (NH2) group through an ethyl chain. It belongs to the 2C family of psychedelics which are known for their hallucinogenic and entheogenic properties. The '2C' designation refers to the two carbon atoms between the benzene ring and the amino group.
Pharmacology[edit]
Like other 2C drugs, N-Ethyl-2C-B acts as a serotonin receptor agonist. It is thought to produce its psychedelic effects by binding to and activating the serotonin 2A receptor, which is found in the brain. However, the exact mechanisms of action are not fully understood.
Effects[edit]
The effects of N-Ethyl-2C-B are similar to those of other 2C drugs. They can include hallucinations, enhanced colors, euphoria, and altered thinking processes. The duration of effects can vary depending on the dose and individual metabolism, but typically last for several hours.
Legal Status[edit]
The legal status of N-Ethyl-2C-B varies by country. In some countries, it is a controlled substance, while in others it is legal to possess and use.
See Also[edit]
References[edit]
<references />

This psychedelic-related article is a stub. You can help WikiMD by expanding it.
-
N-Ethyl-2C-B structure