Ethinylestradiol sulfonate/norethisterone acetate: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 26: | Line 26: | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
{{No image}} | {{No image}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
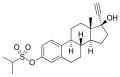
File:Ethinylestradiol sulfonate.svg|Ethinylestradiol sulfonate | |||
File:Norethisterone acetate.svg|Norethisterone acetate | |||
</gallery> | |||
Revision as of 01:05, 20 February 2025
Ethinylestradiol sulfonate/norethisterone acetate is a combined oral contraceptive pill that is used for the prevention of pregnancy. It contains two active ingredients, ethinylestradiol sulfonate and norethisterone acetate, which are synthetic versions of the naturally occurring female sex hormones, estrogen and progesterone.
Etymology
The term "ethinylestradiol" is derived from the words "ethynyl", referring to the ethynyl group present in the chemical structure, and "estradiol", which is a type of estrogen. "Sulfonate" refers to the sulfonate group that is added to the ethinylestradiol to increase its water solubility. "Norethisterone" is derived from "nor-", indicating a demethylated ethisterone, and "ethisterone", a progestin that was used in the first orally effective progestogen-only contraceptive.
Pharmacology
Ethinylestradiol sulfonate is a synthetic estrogen that works by preventing the release of an egg from the ovaries. Norethisterone acetate is a synthetic progestogen that works by thickening the mucus in the cervix, making it difficult for sperm to reach an egg, and thinning the lining of the womb, making it less likely for a fertilized egg to implant and grow.
Usage
This medication is taken orally, usually once a day. It is important to take it at the same time each day to ensure consistent levels of the hormones in the body. If a dose is missed, it should be taken as soon as remembered, and the next dose should be taken at the usual time.
Side Effects
Common side effects of ethinylestradiol sulfonate/norethisterone acetate include nausea, vomiting, headache, bloating, breast tenderness, and weight change. Serious side effects are rare, but may include blood clots, stroke, and heart attack.