Betamethadol: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 20: | Line 20: | ||
{{medicine-stub}} | {{medicine-stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
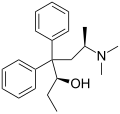
File:Betamethadol.svg|Betamethadol | |||
File:Betamethadol molecule ball.png|Betamethadol molecule ball | |||
</gallery> | |||
Revision as of 00:47, 20 February 2025
Betamethadol is a synthetic opioid analgesic that is part of the phenylpiperidine class of opioids. It is chemically related to methadone and is used in the treatment of severe pain. Betamethadol has a high potential for addiction and is classified as a Schedule II controlled substance in the United States.
Pharmacology
Betamethadol acts on the mu opioid receptor in the central nervous system to produce analgesia. It also has effects on the kappa opioid receptor and the delta opioid receptor, which may contribute to its analgesic effects. Betamethadol is metabolized in the liver by the cytochrome P450 enzyme system.
Clinical Use
Betamethadol is used in the treatment of severe pain, such as that associated with cancer or major surgery. It is typically administered orally, but can also be given by injection. Due to its high potential for addiction, it is usually reserved for use in patients who have not responded to other, less potent opioids.
Side Effects
Common side effects of betamethadol include nausea, vomiting, constipation, and drowsiness. More serious side effects can include respiratory depression, addiction, and overdose. Patients taking betamethadol should be closely monitored for signs of these serious side effects.
See Also
-
Betamethadol
-
Betamethadol molecule ball