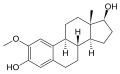
2-Methoxyestradiol: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 34: | Line 34: | ||
[[Category:Antineoplastic drugs]] | [[Category:Antineoplastic drugs]] | ||
[[Category:Hormones]] | [[Category:Hormones]] | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:2-Methoxyestradiol.svg|2-Methoxyestradiol | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 00:35, 20 February 2025
2-Methoxyestradiol[edit]

2-Methoxyestradiol (2-ME) is a naturally occurring estrogen metabolite that has been studied for its potential therapeutic effects, particularly in the context of cancer treatment. It is a derivative of estradiol, one of the primary female sex hormones.
Chemical Properties[edit]
2-Methoxyestradiol is a methoxy derivative of estradiol, specifically at the 2-carbon position. This modification significantly alters its biological activity compared to estradiol itself. The chemical formula of 2-Methoxyestradiol is C19H26O3.
Biological Activity[edit]
2-Methoxyestradiol has been shown to have anti-angiogenic and anti-proliferative effects. It inhibits the formation of new blood vessels, a process known as angiogenesis, which is crucial for tumor growth and metastasis. Additionally, 2-ME disrupts the microtubule network within cells, leading to cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in cancer cells.
Mechanism of Action[edit]
The mechanism by which 2-Methoxyestradiol exerts its effects involves multiple pathways. It binds to tubulin, inhibiting microtubule polymerization, which is essential for mitosis. This disruption leads to the activation of p53 and caspase pathways, promoting apoptosis. Furthermore, 2-ME downregulates hypoxia-inducible factor 1-alpha (HIF-1_), reducing the expression of pro-angiogenic factors.
Clinical Applications[edit]
Research into 2-Methoxyestradiol has focused on its potential as an anti-cancer agent. It has been investigated in various clinical trials for its efficacy against different types of cancer, including breast cancer, prostate cancer, and ovarian cancer. However, its clinical development has faced challenges due to issues with bioavailability and metabolism.
Synthesis and Metabolism[edit]
2-Methoxyestradiol is synthesized in the body from estradiol through the action of catechol-O-methyltransferase (COMT). This enzyme catalyzes the methylation of the 2-hydroxyl group of estradiol, resulting in the formation of 2-ME. The metabolism of 2-ME involves further conjugation reactions, leading to its excretion.
Safety and Side Effects[edit]
While 2-Methoxyestradiol is generally considered to have a favorable safety profile, some studies have reported side effects such as nausea, fatigue, and dizziness. The compound's impact on hormonal balance and its potential interactions with other medications are areas of ongoing research.
Related Pages[edit]
-
2-Methoxyestradiol