Amarogentin: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
File:Amarogentin_gentiopicrin.png|Amarogentin gentiopicrin | File:Amarogentin_gentiopicrin.png|Amarogentin gentiopicrin | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
== Amarogentin == | |||
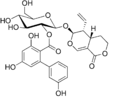
'''Amarogentin''' is a naturally occurring [[iridoid]] glycoside, primarily found in the roots of the plant ''[[Gentiana lutea]]'', commonly known as the yellow gentian. It is renowned for its intensely bitter taste and is one of the most bitter compounds known. | |||
== Chemical Structure == | |||
Amarogentin is classified as a secoiridoid glycoside. Its chemical structure consists of a secoiridoid core linked to a glucose moiety. The bitterness of amarogentin is attributed to its specific molecular configuration, which interacts with taste receptors on the human tongue. | |||
== Biological Activity == | |||
Amarogentin has been studied for its potential [[pharmacological]] properties. It exhibits a range of biological activities, including: | |||
* '''Antimicrobial Activity''': Amarogentin has shown effectiveness against certain strains of [[bacteria]] and [[fungi]], making it a compound of interest in the development of new antimicrobial agents. | |||
* '''Antioxidant Properties''': The compound has demonstrated the ability to scavenge free radicals, suggesting its potential role in reducing oxidative stress and protecting cells from damage. | |||
* '''Anticancer Potential''': Preliminary studies have indicated that amarogentin may have cytotoxic effects on certain [[cancer]] cell lines, although further research is needed to fully understand its mechanisms and potential therapeutic applications. | |||
== Uses in Traditional Medicine == | |||
In traditional [[herbal medicine]], amarogentin-containing plants like ''Gentiana lutea'' have been used for their digestive benefits. The bitter taste of amarogentin is believed to stimulate the production of [[digestive enzymes]] and [[bile]], aiding in digestion and improving appetite. | |||
== Related Compounds == | |||
Amarogentin is related to other bitter compounds found in the Gentianaceae family, such as [[gentiopicroside]] and [[swertiamarin]]. These compounds share similar bitter properties and are often studied together for their potential health benefits. | |||
== Related Pages == | |||
* [[Gentiana lutea]] | |||
* [[Iridoid]] | |||
* [[Bitter taste receptor]] | |||
* [[Phytochemistry]] | |||
{{Gentianaceae}} | |||
[[Category:Iridoid glycosides]] | |||
[[Category:Phytochemicals]] | |||
[[Category:Traditional medicine]] | |||
Latest revision as of 00:40, 19 February 2025
- Amarogentin
-
Amarogentin
-
3D structure of Amarogentin
-
Amarogentin gentiopicrin
Amarogentin[edit]
Amarogentin is a naturally occurring iridoid glycoside, primarily found in the roots of the plant Gentiana lutea, commonly known as the yellow gentian. It is renowned for its intensely bitter taste and is one of the most bitter compounds known.
Chemical Structure[edit]
Amarogentin is classified as a secoiridoid glycoside. Its chemical structure consists of a secoiridoid core linked to a glucose moiety. The bitterness of amarogentin is attributed to its specific molecular configuration, which interacts with taste receptors on the human tongue.
Biological Activity[edit]
Amarogentin has been studied for its potential pharmacological properties. It exhibits a range of biological activities, including:
- Antimicrobial Activity: Amarogentin has shown effectiveness against certain strains of bacteria and fungi, making it a compound of interest in the development of new antimicrobial agents.
- Antioxidant Properties: The compound has demonstrated the ability to scavenge free radicals, suggesting its potential role in reducing oxidative stress and protecting cells from damage.
- Anticancer Potential: Preliminary studies have indicated that amarogentin may have cytotoxic effects on certain cancer cell lines, although further research is needed to fully understand its mechanisms and potential therapeutic applications.
Uses in Traditional Medicine[edit]
In traditional herbal medicine, amarogentin-containing plants like Gentiana lutea have been used for their digestive benefits. The bitter taste of amarogentin is believed to stimulate the production of digestive enzymes and bile, aiding in digestion and improving appetite.
Related Compounds[edit]
Amarogentin is related to other bitter compounds found in the Gentianaceae family, such as gentiopicroside and swertiamarin. These compounds share similar bitter properties and are often studied together for their potential health benefits.