Fusiform gyrus: Difference between revisions
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
CSV import |
||
| Line 32: | Line 32: | ||
[[Category:Brain]] | [[Category:Brain]] | ||
{{neuroscience-stub}} | {{neuroscience-stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
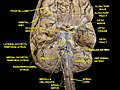
File:Gray727_fusiform_gyrus.png|Fusiform gyrus | |||
File:Medial_surface_of_cerebral_cortex_-_fusiform_gyrus.png|Fusiform gyrus | |||
File:Fusiform_Gyrus_on_3D-printed_brain,_inferior_view.png|Fusiform gyrus | |||
File:Fusiform_Gyrus_and_its_Sulci_on_3D-printed_brain,_inferior_view.png|Fusiform gyrus | |||
File:Slide10ee.JPG|Fusiform gyrus | |||
File:Fusiform_gyrus_animation.gif|Fusiform gyrus | |||
File:Slide2PIT.JPG|Fusiform gyrus | |||
File:Sobo_1909_629.png|Fusiform gyrus | |||
File:Sobo_1909_630.png|Fusiform gyrus | |||
File:Fusiform_-_DK_ATLAS_05.png|Fusiform gyrus | |||
File:Fusiform_gyrus.gif|Fusiform gyrus | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 12:25, 18 February 2025
Fusiform Gyrus
The Fusiform gyrus is a part of the brain located in the temporal lobe and occipital lobe. It is also known as the lateral occipitotemporal gyrus and is named for its unique fusiform, or spindle-shaped, appearance.
Anatomy[edit]
The fusiform gyrus is part of the cerebral cortex and is located between the lingual gyrus and the parahippocampal gyrus. It extends from the anterior part of the temporal lobe to the posterior part of the occipital lobe. The fusiform gyrus is part of the ventral stream of visual processing, also known as the "what pathway", which is involved in object recognition and face perception.
Function[edit]
The primary function of the fusiform gyrus is involved in high-level visual processing and is critical for the recognition of faces, a process known as face perception. This is due to the presence of the fusiform face area (FFA), a region of the fusiform gyrus that shows a particular activation when viewing faces.
The fusiform gyrus is also involved in the processing of color information, word recognition, and within-category identification, such as distinguishing between different types of birds or cars.
Clinical significance[edit]
Damage or abnormalities in the fusiform gyrus can lead to a condition known as prosopagnosia, or face blindness, where individuals are unable to recognize faces. This condition demonstrates the critical role the fusiform gyrus plays in face perception.
In addition, the fusiform gyrus has been implicated in conditions such as autism, dyslexia, and phobias. Research has shown that individuals with autism may have reduced activity in the fusiform gyrus, which could contribute to difficulties in social interaction and communication.
See also[edit]

This article is a neuroscience stub. You can help WikiMD by expanding it!
-
Fusiform gyrus
-
Fusiform gyrus
-
Fusiform gyrus
-
Fusiform gyrus
-
Fusiform gyrus
-
Fusiform gyrus
-
Fusiform gyrus
-
Fusiform gyrus
-
Fusiform gyrus
-
Fusiform gyrus
-
Fusiform gyrus