Polyp (medicine): Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 53: | Line 53: | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:Polyp-2.jpeg|Polyp (medicine) | |||
File:Pie_chart_of_colorectal_polyp_etiologies.png|Pie chart of colorectal polyp etiologies | |||
File:Pie_chart_of_relative_incidences_of_gastric_polyps.png|Pie chart of relative incidences of gastric polyps | |||
File:Hyperplastic_polyp1.jpg|Hyperplastic polyp | |||
File:Histopathology_of_a_gastric_hyperplastic_polyp.jpg|Histopathology of a gastric hyperplastic polyp | |||
File:Fundic_Gland_Polyp,_Stomach_(3295692096).jpg|Fundic Gland Polyp, Stomach | |||
File:Sessile_serrated_adenoma3.jpg|Sessile serrated adenoma | |||
File:Tubular_adenoma_2_high_mag.jpg|Tubular adenoma | |||
File:Traditional_serrated_adenoma_intermed_mag.jpg|Traditional serrated adenoma | |||
File:Peutz-Jeghers_syndrome_polyp.jpg|Peutz-Jeghers syndrome polyp | |||
File:Gastric_juvenile_polyp_-_2_-_very_low_mag.jpg|Gastric juvenile polyp | |||
File:Inflammatory_fibroid_polyp_-_intermed_mag.jpg|Inflammatory fibroid polyp | |||
</gallery> | |||
Revision as of 12:24, 18 February 2025
Polyp (medicine)
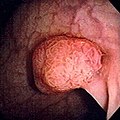
A Polyp is an abnormal growth of tissue projecting from a mucous membrane. If it is attached to the surface by a narrow elongated stalk, it is said to be pedunculated; if it is attached without a stalk, it is said to be sessile. Polyps are commonly found in the colon, stomach, nose, ear, sinus(es), urinary bladder, and uterus. They may also occur elsewhere in the body where mucous membranes exist like the cervix, vocal folds, and small intestine.
Types of Polyps
There are several types of polyps that occur in different areas of the body and have varying characteristics. Some of these include:
- Adenomatous polyps: These are polyps that occur in the colon and are a pre-cancerous condition.
- Hyperplastic polyps: These are typically benign and occur in the colon.
- Inflammatory polyps: These occur as a result of inflammation in the colon.
- Hamartomatous polyps: These are benign and can occur in several parts of the body.
- Neoplastic polyps: These are polyps that have the potential to become cancerous.
Symptoms
Polyps may not cause symptoms, but if they do, they may include:
Diagnosis
Polyps are diagnosed through a variety of methods, including:
Treatment
Treatment for polyps depends on their location, size, and whether they are benign or malignant. Treatment options may include:
See Also
|
|
|
-
Polyp (medicine)
-
Pie chart of colorectal polyp etiologies
-
Pie chart of relative incidences of gastric polyps
-
Hyperplastic polyp
-
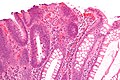
Histopathology of a gastric hyperplastic polyp
-
Fundic Gland Polyp, Stomach
-
Sessile serrated adenoma
-
Tubular adenoma
-
Traditional serrated adenoma
-
Peutz-Jeghers syndrome polyp
-
Gastric juvenile polyp
-
Inflammatory fibroid polyp