Isatin: Difference between revisions
CSV import Tags: Manual revert mobile edit mobile web edit |
CSV import |
||
| Line 34: | Line 34: | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:Sendmeyer_synthesis_of_Isatin.jpg|Sendmeyer synthesis of Isatin | |||
File:Stolle_synthesis_of_Isatin.jpg|Stolle synthesis of Isatin | |||
File:Oxidation_synthesis_of_Isatin.jpg|Oxidation synthesis of Isatin | |||
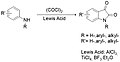
File:Isatin_N-alkylation,_acylation.jpg|Isatin N-alkylation, acylation | |||
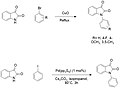
File:Isatin_Arylation.jpg|Isatin Arylation | |||
File:Isatin_ring_expansion.jpg|Isatin ring expansion | |||
File:Isatin_ring_expansion1.jpg|Isatin ring expansion | |||
File:Isatin_nuclophilic_addition.jpg|Isatin nucleophilic addition | |||
File:Isatin_oxidation.jpg|Isatin oxidation | |||
File:Isatin_dimerization.jpg|Isatin dimerization | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 11:43, 18 February 2025
Isatin is an organic compound with the molecular formula C8H5NO2. It is an indole derivative, specifically an oxindole, and is a yellowish to orange solid. Isatin is a versatile molecule that has been used as a starting material in the synthesis of a wide variety of chemical compounds, including pharmaceuticals, dyes, and agrochemicals.
History[edit]
Isatin was first discovered in 1841 by the German chemist Friedrich Wöhler and the Swiss chemist Justus von Liebig. They isolated it from indigo dye, a natural dye that has been used for thousands of years. The name "isatin" comes from the Greek word "isatis", which means "indigo".
Properties and structure[edit]
Isatin is a crystalline solid that is yellowish to orange in color. It has a melting point of 200-202 °C and a boiling point of 389.8 °C at 760 mmHg. It is soluble in ethanol, acetone, and hot water, but insoluble in cold water and petroleum ether.
The structure of isatin is based on the indole skeleton, which consists of a benzene ring fused to a pyrrole ring. In isatin, the pyrrole ring is further modified to an oxindole, meaning it contains an oxygen atom. The molecule also contains a carbonyl group and a nitrogen atom, which contribute to its reactivity.
Synthesis[edit]
Isatin can be synthesized from indigo dye by oxidation with nitric acid. This is the method that was originally used by Wöhler and Liebig. However, there are now many other methods available for the synthesis of isatin, including the Sandmeyer isatin synthesis, the Gassman isatin synthesis, and the Japp-Klingemann reaction.
Applications[edit]
Isatin is a versatile starting material in organic synthesis. It has been used to synthesize a wide variety of chemical compounds, including pharmaceuticals, dyes, and agrochemicals. Some of the pharmaceuticals that have been synthesized from isatin include oxindole, isatinic acid, and isatinic anhydride.
See also[edit]
References[edit]
<references />
|
|
|
-
Sendmeyer synthesis of Isatin
-
Stolle synthesis of Isatin
-
Oxidation synthesis of Isatin
-
Isatin N-alkylation, acylation
-
Isatin Arylation
-
Isatin ring expansion
-
Isatin ring expansion
-
Isatin nucleophilic addition
-
Isatin oxidation
-
Isatin dimerization