Ontogeny: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 39: | Line 39: | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
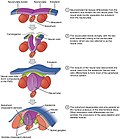
File:HumanEmbryogenesis.svg|Human Embryogenesis Diagram | |||
File:Human_embryo_8_weeks_2.JPG|Human Embryo at 8 Weeks | |||
File:Figure_27_01_03.jpg|Developmental Stages | |||
File:Blastula.png|Blastula Stage | |||
File:Germ_layers.jpg|Germ Layers | |||
File:Ernst_Haeckel,_Anthropogenie._Wellcome_L0027291.jpg|Ernst Haeckel's Anthropogenie | |||
File:2912_Neurulation-02.jpg|Neurulation Process | |||
File:Acraea_zetes_caterpillar_to_pupae_to_butterfly_metamorphosis_by_Nick_Hobgood.jpg|Acraea zetes Metamorphosis | |||
</gallery> | |||
Revision as of 11:36, 18 February 2025
Ontogeny refers to the development of an individual organism or anatomical or behavioral feature from the earliest stage to maturity. The term is derived from two Greek words, "ontos" meaning "being" and "geneia" meaning "origin". The concept of ontogeny is central to the field of developmental biology.
History
The concept of ontogeny has been around since the 19th century, with the term being coined by the German biologist Ernst Haeckel. Haeckel proposed a theory known as the biogenetic law, which states that the development of an individual organism (its ontogeny) recapitulates the evolutionary development of its species (its phylogeny).
Ontogeny and Phylogeny
Ontogeny and phylogeny are two fundamental aspects of biological development and evolution. While ontogeny deals with the development of an individual organism, phylogeny deals with the evolutionary history of a species or group of related species. The relationship between ontogeny and phylogeny has been a subject of scientific debate and research for many years.
Ontogenetic Development
Ontogenetic development involves various stages, starting from the fertilization of the egg (zygote) to the maturity of the organism. These stages include embryogenesis, morphogenesis, and organogenesis. Each stage involves complex biological processes and is regulated by various genetic and environmental factors.
Ontogeny in Different Organisms
The process of ontogeny varies greatly among different organisms. In mammals, for example, ontogeny involves the development of the embryo inside the mother's womb, while in birds and reptiles, it involves the development of the embryo inside an egg. In plants, ontogeny involves the development of the plant from a seed.
Ontogeny and Evolution
The study of ontogeny can provide valuable insights into the process of evolution. By studying the developmental processes of different organisms, scientists can gain a better understanding of how these organisms have evolved over time.
See Also
References
<references />