Propionyl-CoA: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 20: | Line 20: | ||
[[Category:Metabolism]] | [[Category:Metabolism]] | ||
[[Category:Coenzymes]] | [[Category:Coenzymes]] | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:Propionyl-Coenzyme_A.png|Propionyl-Coenzyme A structure | |||
File:Odd-chain_FA_oxydation.png|Odd-chain fatty acid oxidation | |||
File:Nihms213291f1.jpg|Propionyl-CoA | |||
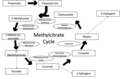
File:Methylcitrate_Cycle_with_Intermediates_and_Enzymes.png|Methylcitrate cycle with intermediates and enzymes | |||
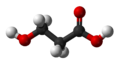
File:3-hydroxypropionic-acid-3D-balls.png|3-Hydroxypropionic acid 3D model | |||
File:Aspergillus_nidulans.jpg|Aspergillus nidulans | |||
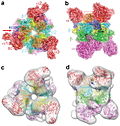
File:5H84_as_recorded_by_PYMOL_from_the_Protein_Data_Bank.png|5H84 structure from the Protein Data Bank | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 11:34, 18 February 2025
Propionyl-CoA is a significant intermediate in the metabolic pathway known as the tricarboxylic acid cycle (TCA cycle) or Krebs cycle. It is derived from the catabolism of odd-chain fatty acids, branched-chain amino acids, and from the side chain of cholesterol.
Structure[edit]
Propionyl-CoA is a Coenzyme A (CoA) derivative in which the terminal sulfhydryl group (-SH) is linked to the carboxyl group (-COOH) of propionic acid through a high-energy thioester bond. The molecule is composed of an adenosine 3',5'-bisphosphate moiety, a pantothenic acid moiety, and a cysteamine moiety.
Metabolism[edit]
Propionyl-CoA is metabolized in a series of reactions known as the propionyl-CoA carboxylase pathway. This pathway converts propionyl-CoA to methylmalonyl-CoA, which is then converted to succinyl-CoA, a key intermediate in the TCA cycle. The conversion of propionyl-CoA to succinyl-CoA requires several enzymes and cofactors, including biotin, adenosylcobalamin, and methylmalonyl-CoA mutase.
Clinical significance[edit]
Defects in the metabolism of propionyl-CoA can lead to several metabolic disorders, including propionic acidemia and methylmalonic acidemia. These disorders are characterized by the accumulation of propionyl-CoA and its metabolites in the body, leading to various symptoms such as developmental delay, intellectual disability, and metabolic acidosis.
See also[edit]

This article is a biochemistry stub. You can help WikiMD by expanding it!
-
Propionyl-Coenzyme A structure
-
Odd-chain fatty acid oxidation
-
Propionyl-CoA
-
Methylcitrate cycle with intermediates and enzymes
-
3-Hydroxypropionic acid 3D model
-
Aspergillus nidulans
-
5H84 structure from the Protein Data Bank