Frankincense: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 32: | Line 32: | ||
[[Category:Traditional medicine]] | [[Category:Traditional medicine]] | ||
[[Category:Aromatherapy]] | [[Category:Aromatherapy]] | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:Frankincense_2005-12-31.jpg|Frankincense | |||
File:Boswellia-sacra-greenhouse.jpg|Boswellia sacra in greenhouse | |||
File:Boswellia_sacra.jpg|Boswellia sacra | |||
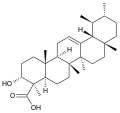
File:Beta-boswellic_acid.svg|Chemical structure of Beta-boswellic acid | |||
File:Weihrauch.jpg|Weihrauch (Frankincense) | |||
File:Olibanum_resin.jpg|Olibanum resin | |||
File:Olebanum.jpg|Olebanum | |||
File:Dabqaad.jpg|Dabqaad (traditional incense burner) | |||
File:FrankinsenceEssOil.png|Frankincense essential oil | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 11:23, 18 February 2025
Frankincense is a type of resin obtained from trees of the genus Boswellia in the family Burseraceae. It is used in incense and perfumes, and has been valued for its aromatic properties for thousands of years.
History[edit]
Frankincense has been traded on the Arabian Peninsula and in North Africa for more than 5000 years. The Ancient Egyptians used it in their religious rituals, and it is mentioned in the Bible as one of the gifts brought to the baby Jesus by the Three Wise Men.
Production[edit]
Frankincense is produced by making a deep, longitudinal incision in the trunk of the Boswellia tree. The resin that exudes is allowed to harden and is then scraped off. The process is repeated several times until the tree produces no more resin.
Uses[edit]
Frankincense is used in traditional medicine in many cultures. It is believed to have anti-inflammatory, antiseptic, and astringent properties. It is also used in aromatherapy for its calming effect.
See also[edit]
References[edit]
<references />