Glia: Difference between revisions
From WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
CSV import |
||
| Line 39: | Line 39: | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:Glial_Cell_Types.png|Glial Cell Types | |||
File:Neuroglia.png|Neuroglia | |||
File:Gfapastr5.jpg|Glia | |||
File:2010-3-15_rGFAP_1-4000_1-200_Hip_20x(4).jpg|Glia | |||
File:Blausen_0870_TypesofNeuroglia.png|Types of Neuroglia | |||
File:Human_astrocyte.png|Human Astrocyte | |||
File:Anaplastic_astrocytoma_-_gfap_-_very_high_mag.jpg|Anaplastic Astrocytoma | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 11:23, 18 February 2025
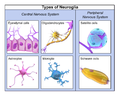
Glia or glial cells are non-neuronal cells in the central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system. They maintain homeostasis, form myelin, and provide support and protection for neurons. In the central nervous system, glial cells include oligodendrocytes, astrocytes, ependymal cells, and microglia, and in the peripheral nervous system, glial cells include Schwann cells and satellite cells.
Function[edit]
Glia have four main functions:
- To surround neurons and hold them in place,
- To supply nutrients and oxygen to neurons,
- To insulate one neuron from another,
- To destroy pathogens and remove dead neurons.
Types of Glial Cells[edit]
Central Nervous System[edit]
- Oligodendrocytes - These cells produce the myelin sheath, a fatty layer that insulates nerve fibers in the central nervous system.
- Astrocytes - These are star-shaped cells that provide physical and nutritional support for neurons.
- Ependymal Cells - These cells line the ventricles of the brain and the central canal of the spinal cord.
- Microglia - These are the immune cells of the central nervous system.
Peripheral Nervous System[edit]
- Schwann Cells - These cells produce the myelin sheath in the peripheral nervous system.
- Satellite Cells - These cells surround the neuron cell bodies in the ganglia of the peripheral nervous system.
Diseases Related to Glia[edit]
Glia are involved in a number of neurological disorders, including multiple sclerosis, Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, and Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis.