Correlation: Difference between revisions
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
||
| Line 41: | Line 41: | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
{{dictionary-stub1}} | {{dictionary-stub1}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
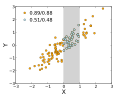
File:Correlation_examples2.svg|Scatter plots showing different types of correlation | |||
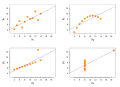
File:Pearson_Correlation_Coefficient_and_associated_scatterplots.png|Pearson Correlation Coefficient and associated scatterplots | |||
File:correlation_range_dependence.svg|Correlation range dependence | |||
File:Anscombe's_quartet_3.svg|Anscombe's quartet | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 05:02, 18 February 2025
Correlation is a statistical measure that describes the degree to which two variables move in relation to each other. In the field of statistics, correlation is used to measure the strength and direction of the relationship between two variables.
Definition[edit]
Correlation is defined as the statistical relationship between two or more variables that change together, though not necessarily at the same rate. The correlation coefficient is a measure of the strength of this relationship. It is represented by the letter 'r' and can range from -1 to 1.
Types of Correlation[edit]
There are three types of correlation: positive, negative, and zero correlation.
- Positive Correlation: When the values of both variables increase or decrease together, the correlation is said to be positive.
- Negative Correlation: When the value of one variable increases while the other decreases, the correlation is said to be negative.
- Zero Correlation: When there is no relationship between the variables, the correlation is said to be zero.
Correlation vs Causation[edit]
It is important to note that correlation does not imply causation. Just because two variables correlate does not mean that one causes the other to occur. They may be related due to a third, unseen factor, known as a confounding variable.
Correlation in Medical Research[edit]
In medical research, correlation is used to determine if a relationship exists between two health-related variables, for example, smoking and lung cancer. This can help identify risk factors for diseases and guide public health interventions.
Calculating Correlation[edit]
The correlation between two variables can be calculated using the Pearson correlation coefficient formula. This formula takes into account the standard deviation and mean of both variables.
Limitations of Correlation[edit]
While correlation can indicate a possible relationship between two variables, it does not prove a cause-and-effect relationship. Correlation also cannot measure non-linear relationships, only linear ones.