Equivalent dose: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 35: | Line 35: | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:Dose_quantities_and_units.png|Equivalent_dose | |||
File:SI_Radiation_dose_units.png|Equivalent_dose | |||
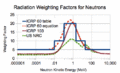
File:Neutron_radiation_weighting_factor_as_a_function_of_kinetic_energy.gif|Equivalent_dose | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 04:12, 18 February 2025
Equivalent dose is a dose quantity H representing the stochastic health effects of low levels of ionizing radiation on the human body which represents the probability of radiation-induced cancer and genetic damage. It is measured in sieverts (Sv).
Definition[edit]
The equivalent dose is the mean dose to organ T by radiation type R (DT,R), multiplied by a weighting factor WR. This designed to account for the different effectiveness of the various types of radiation to cause biological damage, and is an international convention as part of the System of Radiological Protection by the International Commission on Radiological Protection (ICRP).
Calculation[edit]
The equivalent dose (HT) to a tissue or organ is found by summing the mean organ dose due to each radiation type R (DT,R), multiplied by the radiation weighting factor WR. This is given by the formula:
HT = ΣR WR DT,R
Radiation weighting factor[edit]
The radiation weighting factor WR is a dimensionless factor used to determine the equivalent dose from the absorbed dose averaged over a tissue or organ and is based on the type and energy of the radiation incident on the body. The ICRP defines it as:
WR = Dose equivalent (HT) / Absorbed dose (DT)
Units[edit]
The SI unit for equivalent dose is the sievert (Sv). Non-SI units include the rem, which is equal to 0.01 Sv.
See also[edit]
References[edit]
<references />