Furegrelate: Difference between revisions
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
CSV import |
||
| Line 31: | Line 31: | ||
{{medicine-stub}} | {{medicine-stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:Furegrelate_image.png|Furegrelate | |||
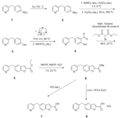
File:Furegrelate_synthetic_pathway.png|Furegrelate synthetic pathway | |||
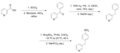
File:Furgrelate_precursor_synthetic_pathway.png|Furegrelate precursor synthetic pathway | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 03:48, 18 February 2025
Furegrelate is a pharmacological agent that belongs to the class of drugs known as thromboxane inhibitors. It is primarily used in the prevention and treatment of thrombosis, a condition characterized by the formation of blood clots within the blood vessels.
Mechanism of Action[edit]
Furegrelate works by inhibiting the synthesis of thromboxane A2, a substance that plays a crucial role in platelet aggregation and vasoconstriction. By blocking the production of thromboxane A2, furegrelate prevents the clumping together of platelets, thereby reducing the risk of clot formation.
Clinical Uses[edit]
Furegrelate is used in the management of conditions that are associated with an increased risk of thrombosis, such as coronary artery disease, stroke, and peripheral artery disease. It may also be used in patients who have undergone angioplasty or stent placement to prevent clot formation and restenosis.
Side Effects[edit]
Like all drugs, furegrelate can cause side effects. These may include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and abdominal pain. In rare cases, it may cause bleeding or bruising. Patients should be monitored closely for these side effects during treatment.
Contraindications[edit]
Furegrelate is contraindicated in patients with a known allergy to the drug. It should also be used with caution in patients with a history of bleeding disorders or those who are taking other anticoagulants or antiplatelet drugs.
Drug Interactions[edit]
Furegrelate may interact with other drugs, including other anticoagulants, antiplatelet drugs, and certain antidepressants. These interactions can increase the risk of bleeding and should be avoided.
Dosage and Administration[edit]
The dosage of furegrelate is determined by the treating physician based on the patient's condition and response to treatment. It is usually taken orally, with or without food.
See Also[edit]
-
Furegrelate
-
Furegrelate synthetic pathway
-
Furegrelate precursor synthetic pathway