Pierre Robin sequence: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 29: | Line 29: | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
{{dictionary-stub1}} | {{dictionary-stub1}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:Pierre_Robin_Syndrome_1.jpg|Pierre Robin sequence | |||
File:Pierre_Robin_Syndrome_3.jpg|Pierre Robin sequence | |||
File:Pierre_Robin_Syndrome_4.jpg|Pierre Robin sequence | |||
</gallery> | |||
Revision as of 03:48, 18 February 2025
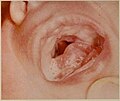
Pierre Robin sequence (also known as Pierre Robin syndrome or Pierre Robin malformation) is a condition present at birth, in which the infant has a smaller than normal lower jaw (micrognathia), a tongue that falls back in the throat and obstructs the airway (glossoptosis), and difficulty breathing. Some children with Pierre Robin sequence may also have a cleft palate.
Causes
The exact cause of Pierre Robin sequence is unknown. It is believed to occur when the lower jaw does not grow properly during fetal development. This causes the tongue to be positioned at the back of the mouth, which can block the airway and cause difficulty breathing. In some cases, Pierre Robin sequence may be associated with genetic conditions or syndromes, such as Stickler syndrome or Velocardiofacial syndrome.
Symptoms
The main symptoms of Pierre Robin sequence are a smaller than normal lower jaw, a tongue that falls back in the throat, and difficulty breathing. Other symptoms may include feeding difficulties, failure to thrive, and ear infections. Some children with Pierre Robin sequence may also have a cleft palate.
Diagnosis
Pierre Robin sequence is usually diagnosed at birth based on the physical characteristics of the infant. Additional tests may be performed to confirm the diagnosis and to check for any associated conditions or complications. These may include a physical examination, imaging tests such as X-rays or CT scans, and genetic testing.
Treatment
The treatment for Pierre Robin sequence depends on the severity of the symptoms and the presence of any associated conditions or complications. Treatment options may include positioning the infant in a way that helps to keep the airway open, surgery to correct the jaw or cleft palate, and therapies to help with feeding and speech development.
Prognosis
The prognosis for children with Pierre Robin sequence varies. With early diagnosis and appropriate treatment, most children can lead normal lives. However, some children may have ongoing difficulties with breathing, feeding, and speech.