Caryopsis: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 21: | Line 21: | ||
{{Botany-stub}} | {{Botany-stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:Assorted_grains.jpg|Assorted grains | |||
File:Spiklet.jpg|Spiklet | |||
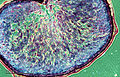
File:Caryopsis_(grain)_(255_31)_Cross-section.jpg|Caryopsis cross-section | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 02:16, 18 February 2025
Caryopsis is a type of fruit commonly referred to as a grain. It is characteristic of the Poaceae family, which includes well-known cereal crops such as wheat, rice, corn, barley, and oats. A caryopsis is distinguished by its simple, dry nature, and unlike many other fruits, it does not split open at maturity. The key feature of a caryopsis is the fusion of the seed coat with the fruit wall, or pericarp, making the seed and fruit indistinguishable.
Characteristics[edit]
The caryopsis is small and hard, adapted for various dispersal mechanisms, including wind and animal ingestion. The outer layer, or pericarp, is fused to the seed coat, a unique characteristic among fruits. This fusion aids in protecting the inner embryo and endosperm, which are crucial for the germination and growth of a new plant. The endosperm within the caryopsis is a significant source of starch, making these grains a vital food source for humans and animals.
Ecological and Economic Importance[edit]
Caryopses are of immense ecological and economic importance. They serve as a primary food source for a significant portion of the world's population. Crops like wheat and rice are staple foods in many cultures, providing essential nutrients and calories. Additionally, these grains are used in various industries, including food production, alcohol brewing, and biofuel manufacturing.
Cultivation[edit]
The cultivation of caryopsis-bearing plants has a long history, with evidence of farming dating back thousands of years. Modern agriculture has developed sophisticated methods for growing, harvesting, and processing these grains, allowing for efficient production to meet global demand. However, challenges such as pests, diseases, and climate change pose ongoing threats to crop yields and food security.
Research and Breeding[edit]
Significant research efforts are dedicated to understanding the genetics and biology of caryopsis-producing plants. These studies aim to improve yield, disease resistance, and nutritional content through traditional breeding and genetic modification. Advances in biotechnology have led to the development of crop varieties that can withstand adverse environmental conditions, such as drought and salinity, which are increasingly important in the face of climate change.
Conclusion[edit]
The caryopsis is a vital component of the human diet and the global economy, with a profound impact on agriculture and food systems worldwide. Ongoing research and development efforts are crucial to ensuring the sustainability and security of these essential food sources.
-
Assorted grains
-
Spiklet
-
Caryopsis cross-section