Demexiptiline: Difference between revisions
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
CSV import |
||
| Line 23: | Line 23: | ||
{{medicine-stub}} | {{medicine-stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
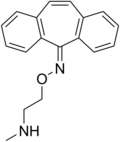
File:Demexiptiline.png|Demexiptiline | |||
File:Demexiptiline-3D-spacefill.png|Demexiptiline 3D Spacefill | |||
File:Demexiptiline_synthesis.svg|Demexiptiline Synthesis | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 01:27, 18 February 2025
Demexiptiline is a tricyclic antidepressant (TCA) that was developed in the 1960s but was never marketed. It is similar in structure and pharmacological effects to other TCAs such as imipramine and desipramine.
Pharmacology[edit]
Demexiptiline acts primarily as a norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor, which means it increases the amount of norepinephrine in the brain by blocking its reabsorption into nerve cells. This can help to alleviate symptoms of depression.
Chemistry[edit]
Demexiptiline is a tricyclic compound, meaning it contains three rings of atoms in its chemical structure. It is part of the dibenzazepine class of TCAs, which also includes imipramine and desipramine.
History[edit]
Demexiptiline was developed in the 1960s as part of a wave of new antidepressant drugs. However, it was never marketed, possibly due to the emergence of newer, safer antidepressants in the following decades.
Side Effects[edit]
Like other TCAs, demexiptiline can cause a range of side effects, including dry mouth, blurred vision, constipation, urinary retention, and orthostatic hypotension. It can also cause mental effects such as confusion, hallucinations, and changes in mood or behavior.
See Also[edit]
This article is a medical stub. You can help WikiMD by expanding it!
-
Demexiptiline
-
Demexiptiline 3D Spacefill
-
Demexiptiline Synthesis