Peristalsis: Difference between revisions
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
CSV import |
||
| Line 27: | Line 27: | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
== Peristalsis == | |||
<gallery> | |||
File:Peristaltic.jpg|Peristalsis | |||
File:Peristalsis.gif|Peristalsis | |||
File:Earthworm_movement_all.jpg|Earthworm movement demonstrating peristalsis | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 01:17, 18 February 2025
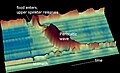
Peristalsis is a radially symmetrical contraction and relaxation of muscles that propagates in a wave down a tube, in an anterograde direction. In much of a digestive tract such as the human gastrointestinal tract, smooth muscle tissue contracts in sequence to produce a peristaltic wave, which propels a ball of food (called a bolus while in the esophagus and upper gastrointestinal tract and chyme in the stomach) along the tract. Peristaltic movement comprises relaxation of circular smooth muscles, then their contraction behind the chewed material to keep it from moving backward, then longitudinal contraction to push it forward.
Causes[edit]
Peristalsis is initiated by the smooth muscle cells located in the walls of the organ. These cells are activated by the autonomic nervous system or by the enteric nervous system. The waves of contraction and relaxation move in one direction only.
Role in the human body[edit]
Peristalsis is a vital process in the human body, playing a key role in the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, the esophagus, and the urinary tract. It is responsible for moving food through the digestive system, and for the passage of waste products from the body.
Disorders[edit]
Disorders of peristalsis can lead to a variety of medical conditions. These include gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), achalasia, and certain types of intestinal obstruction. Treatment for these conditions often involves addressing the underlying cause of the peristaltic dysfunction.
See also[edit]
References[edit]
<references />