Orthodontic archwire: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{DISPLAYTITLE:Orthodontic Archwire}} | |||
== | == Orthodontic Archwire == | ||
Orthodontic | [[File:Week_4_of_braces.jpg|thumb|right|Orthodontic archwire in use with braces]] | ||
An '''orthodontic archwire''' is a wire used in [[orthodontics]] to align and straighten [[teeth]] and help to position them properly in relation to a person's [[bite]], while also working to improve [[dental health]]. It is a critical component of [[dental braces]], which are used to correct [[malocclusion]]s, such as [[overbite]], [[underbite]], [[crossbite]], and [[open bite]]. | |||
== Composition == | |||
Orthodontic archwires are made from various materials, each offering different properties. Common materials include: | |||
* '''[[Stainless steel]]''': Known for its strength and durability, stainless steel is a traditional choice for archwires. | |||
* '''[[Nickel-titanium]] (NiTi)''': This material is known for its shape memory and superelasticity, making it ideal for initial alignment. | |||
* '''[[Beta-titanium]]''': Offers a balance between flexibility and strength, providing more control over tooth movement. | |||
* '''[[Cobalt-chromium]]''': Allows for customization of stiffness and is used in specific clinical situations. | |||
== | == Types of Archwires == | ||
Orthodontic archwires come in various types, each serving a specific purpose in the treatment process: | |||
* '''Round wires''': Typically used in the initial stages of treatment to level and align the teeth. | |||
* '''Rectangular wires''': Used in later stages to control the movement of the teeth more precisely. | |||
* '''Square wires''': Provide a combination of control and flexibility, used in intermediate stages. | |||
== | == Function == | ||
The primary function of an orthodontic archwire is to apply force to the teeth, guiding them into the desired position. The wire is threaded through [[brackets]] attached to each tooth and is secured with [[ligatures]]. As the wire attempts to return to its original shape, it exerts pressure on the teeth, encouraging movement. | |||
== | == Adjustments == | ||
Throughout the course of orthodontic treatment, archwires are periodically adjusted or replaced to continue the movement of the teeth. Adjustments may involve changing the wire's shape, size, or material to achieve the desired outcome. | |||
== Related Pages == | |||
* [[Dental braces]] | |||
* [[Orthodontics]] | |||
* [[Malocclusion]] | |||
* [[Tooth movement]] | |||
[[Category:Orthodontics]] | [[Category:Orthodontics]] | ||
Latest revision as of 11:36, 15 February 2025
Orthodontic Archwire[edit]
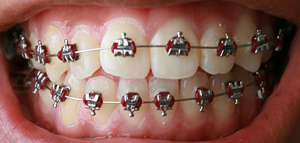
An orthodontic archwire is a wire used in orthodontics to align and straighten teeth and help to position them properly in relation to a person's bite, while also working to improve dental health. It is a critical component of dental braces, which are used to correct malocclusions, such as overbite, underbite, crossbite, and open bite.
Composition[edit]
Orthodontic archwires are made from various materials, each offering different properties. Common materials include:
- Stainless steel: Known for its strength and durability, stainless steel is a traditional choice for archwires.
- Nickel-titanium (NiTi): This material is known for its shape memory and superelasticity, making it ideal for initial alignment.
- Beta-titanium: Offers a balance between flexibility and strength, providing more control over tooth movement.
- Cobalt-chromium: Allows for customization of stiffness and is used in specific clinical situations.
Types of Archwires[edit]
Orthodontic archwires come in various types, each serving a specific purpose in the treatment process:
- Round wires: Typically used in the initial stages of treatment to level and align the teeth.
- Rectangular wires: Used in later stages to control the movement of the teeth more precisely.
- Square wires: Provide a combination of control and flexibility, used in intermediate stages.
Function[edit]
The primary function of an orthodontic archwire is to apply force to the teeth, guiding them into the desired position. The wire is threaded through brackets attached to each tooth and is secured with ligatures. As the wire attempts to return to its original shape, it exerts pressure on the teeth, encouraging movement.
Adjustments[edit]
Throughout the course of orthodontic treatment, archwires are periodically adjusted or replaced to continue the movement of the teeth. Adjustments may involve changing the wire's shape, size, or material to achieve the desired outcome.